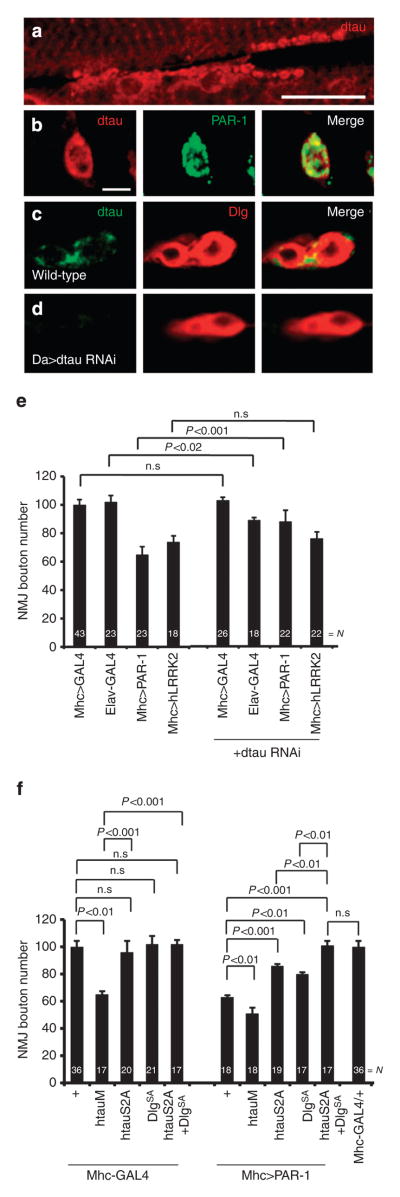
Figure 6. Phospho-dtau mediates the postsynaptic toxicity of PAR-1.
(a–d) Immunostaining showing dtau localization at third instar larval muscle and NMJ. (a) WT larvae stained with anti-dtau antibody shown in red. Scale bar, 50 μm. (b–d) Higher magnification images of NMJ boutons double-labelled with anti-dtau and anti-PAR-1 in WTanimals (b), or labelled with anti-dtau and anti-Dlg in WT (c) and Da-Gal4>dtau-RNAi animals (d). Scale bar, 5 μm. (e) Quantification of NMJ bouton number showing specific genetic interaction between PAR-1 and dtau, but not between hLRRK2 and dtau. N indicates the number of animals analysed. The error bars represent means±s.e.m. P-values were determined using two-tailed Student’s t-test for each comparison. Experiments were performed in triplicate. (f) Quantification of NMJ boutons showing mediation of the postsynaptic effects of PAR-1 by both Dlg and tau. N indicates the number of animals analysed. The error bars represent means±s.e.m. P-values were determined using two-tailed Student’s t-test for each comparison. Experiments were performed in triplicate. n.s, not significant.