Figure 8.
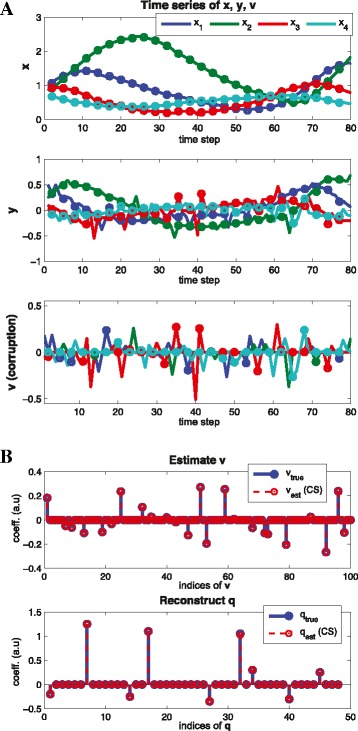
Arbitrary corruption with no measurement noise. (Example 7) Reconstruction with corrupted signal. (A) time series of x,y, v (B) reconstruction results of v and q where each circle represents sampled time points (n=4, M=25, N=12, s=9). By using two-step refinements, first we estimate sparse large corruption v and then, we reconstruct q. Note that since we consider arbitrary corruption, we have more time points (M>N).
