Fig 1.
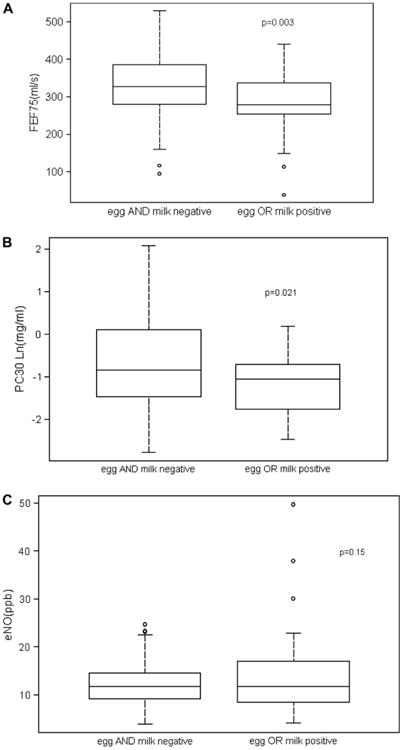
Comparison of infants sensitized to either egg or milk and those infants not sensitized to either egg or milk. Box plots illustrate distribution of data. A, Mean ± SE forced expiratory flows (FEF75) were significantly less in the infants sensitized to egg or milk (336 ± 12 vs 280 ± 16 mL/s, P < .003). B, Mean ± SE PC30 values were significantly less in infants sensitized to egg or milk (−0.6 ± 0.2 vs −1.2 ± 0.2 mg/mL, P < .023). C, Mean ± SE eNO levels were not significantly different for the 2 groups (11.6 ± 1.0 vs 13.8 ± 1.3 ppb, P = .15).
