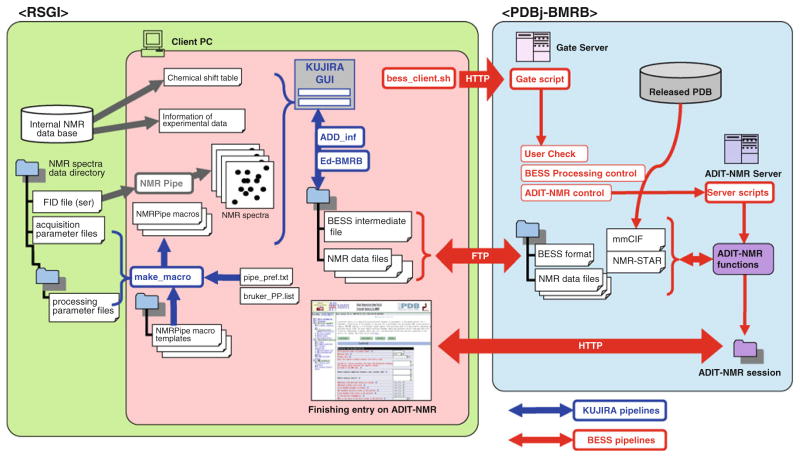
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the system for deposition and annotation of NMR data from RSGI to BMRB. The tools implemented in KUJIRA and BESS and related pipelines for files and tasks are colored blue and red, respectively. According to the preference settings described in the pipe_pref.txt, the program, make_macro, searches for corresponding NMR acquisition data sets in the server. The NMRPipe macro files, fid_*.com, xy_*.com and z_*.com are created for each spectrum from their corresponding template macro files by with the addition of the proper processing parameters such as phasing, extraction and zero-filling points and axis-order. The confirmation of the consensus between the NMR data and the assigned chemical shifts are carried out using the tools implemented in KUJIRA. To translate the retrieved NMR data using BESS, an entry information file is created and downloaded by bess_client.sh on the client PC using a mmCIF file derived from the corresponding released PDB entry. The program “ADD_inf” in KUJIRA fills the required information such as author information, followed by confirmation of consistency of entry information between the intermediate file and the corresponding one in the internal database on the RSGI side. The depositor can upload an entry information file and NMR data to the PDBj-BMRB side via FTP executed by “bess_client.sh”. Then the depositor can remotely execute the “Gate script” which activates “User_Check” and “BESS Processing control” followed by “ADIT-NMR control” to execute “Server scripts” on the ADIT-NMR server. These functions create a virtual ADIT-NMR session. The “bess_client.sh” can also handle HTTP protocol to call and edit the entry information on a web-browser by restarting an ADIT-NMR session