Figure 1. Trypan Blue Microscopy of Cryptococci.
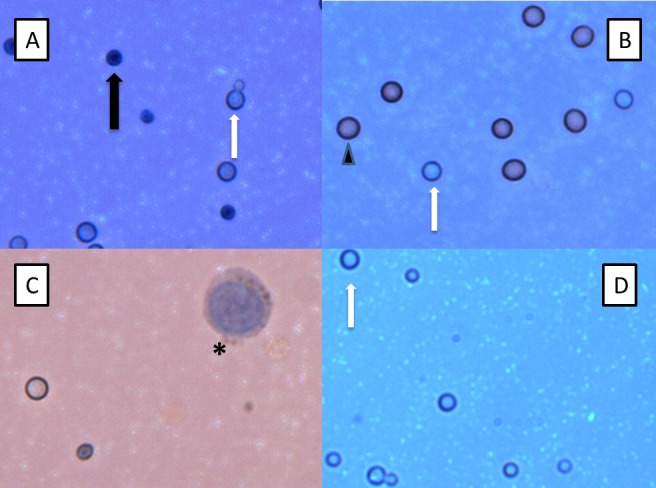
Light microscopic examination of Trypan blue-stained cryptococci at 40x magnification readily distinguishes viable (transparent, white arrow) and dead (dark blue, black arrow) cryptococci in in vitro (A) and CSF (B-D) samples. Note the presence of budding viable cryptococci in (A). Erythrocytes (arrowhead) are also observed in the CSF sample in (B) alongside viable cryptococci. (B), (C) and (D) are CSF samples obtained before and after dilution with water, respectively, which lyses mammalian cells. The large nucleated cell (asterisk) observed before dilution in (C) is a leukocyte. Many viable cryptococci remain in the CSF after lysis of mammalian cells in (D) (white arrow). The different intensity of background colour is due to adjustment of microscopy lighting, focus and contrast. No colour adjustment has been performed post-photography.
