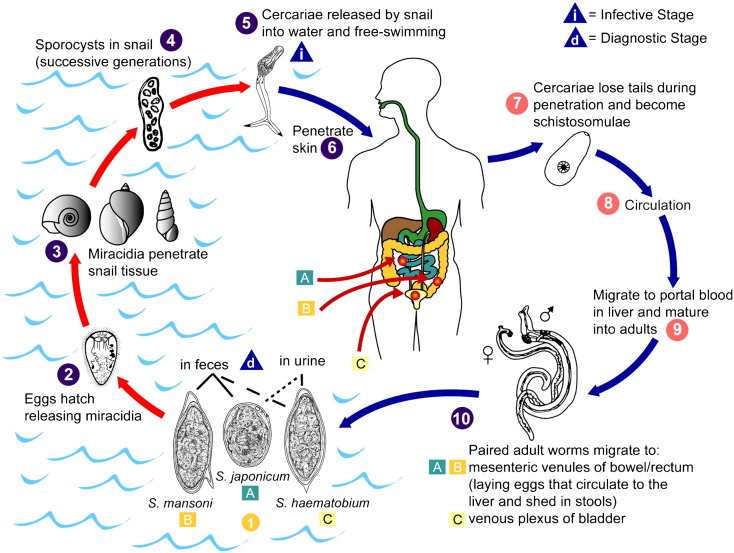
Fig. 1.
Schistosome life cycle. The stages of the schistosome life cycle (1–10) include (1) elimination from the host as eggs in feces or urine (diagnostic stage), (2) hatching of miracidia, (3) infection of species-specific aqueous snail intermediate hosts, (4) proliferation of sporocysts within snails, (5) release of cercariae into water (infective stage), (6) infection of host by skin penetration, (7) development into schistosomulae, (8) circulation, (9) maturation within portal vasculature, and (10) migration of paired adult worms to target organs. Elimination of schistosome eggs in either feces or urine depends on whether the adults reside in the mesenteric venules of the bowel/rectum (primarily (A) Schistosoma japonicum and (B) Schistosoma mansoni) or in the venous plexus of the bladder (primarily (C) Schistosoma haematobium), respectively.
Figure provided by A. J. da Silva and M. Moser for copyright-free dissemination through the Public Health Image Library of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [7].