Fig. 3.
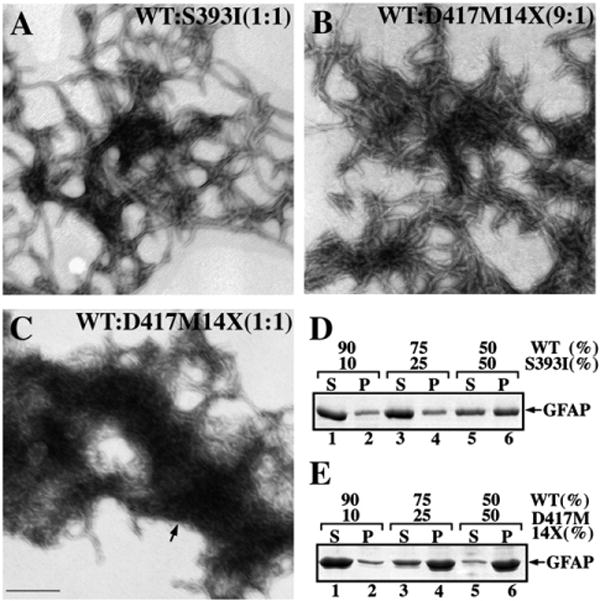
The dominant effect of the GFAP tail mutants revealed by in vitro assembly studies. WT GFAP was coassembled with either S393I (A) or D417M14X (B and C) GFAP in the indicated ratios. After assembly, samples were negatively stained and visualized by TEM. Bar=200 nm. (D, E) Supernatant (S) and pellet (P) fractions from the low speed sedimentation assay were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 staining. Notice that increasing the ratio of mutant GFAP in the assembly mixtures led to an increased GFAP signal in the pellet fractions.
