Fig. 4.
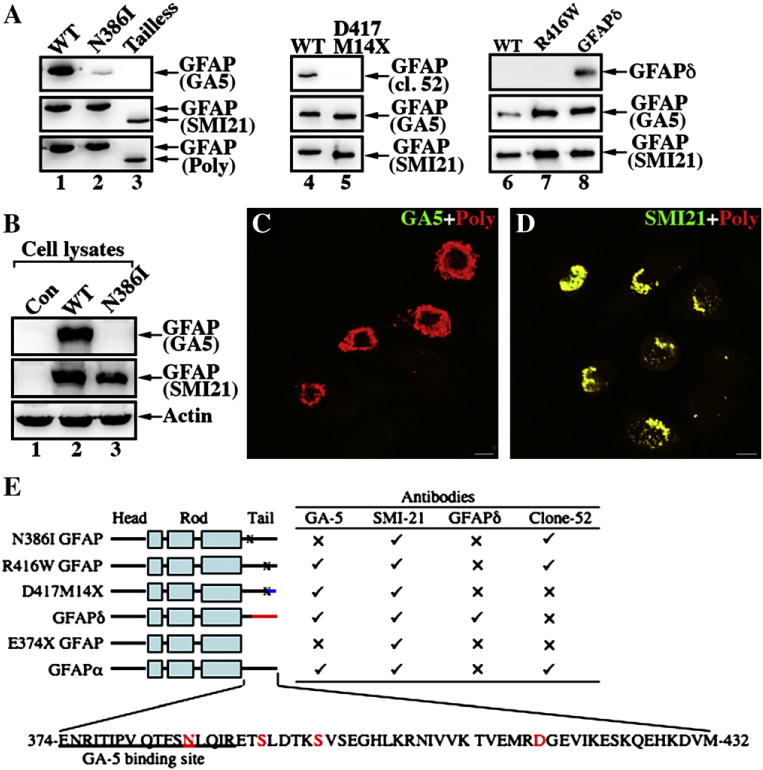
Epitope mapping of a monoclonal antibody GA-5 binding site on GFAP. (A) Purified recombinant GFAP variants were immunoblotted with the indicated anti-GFAP antibodies. The ability of the antibodies to detect WT and mutant GFAP proteins is summarized (E). (✓), Immunopositive; (x), immunonegative. (B) MCF7 cells (B, lane 1; untransfected) were transfected with WT (B, lane 2) or N386I (B, lane 3) GFAP. The total cell lysates were probed with anti-GFAP antibodies as indicated. Notice that the GA5 antibody failed to recognize N386I GFAP (lane 3). (C, D) MCF7 cells transiently transfected with N386I GFAP were fixed 48 h after transfection and visualized by double-label immunofluorescence microscopy. Cells were stained with either GA5 (C, green channel) or SMI-21 (D, green channel) antibody and counterstained with a polyclonal anti-GFAP antibody to reveal transfected cells (C, D; red channel). Merged images are shown. Note that transient expression of N386I GFAP in MCF7 cells resulted in the formation of GFAP-containing aggregates that were readily stained by the SMI antibody and a polyclonalanti-GFAP antibody, but not GA5 antibody. Bar = 10 μm. (E) A schematic view of GFAP structural organization and localization of alterations in the GFAP variants. GFAP comprises a central α-helical rod domain, flanked by non-α-helical head and tail domains (denoted by black bars). Within this rod domain, the heptad repeat-containing segments (denoted by boxes) are separated by short linker sequences (denoted by black bars). The blue (D417M14X with 14 novel residues after the codon 417) and red (GFAPδ with 42 novel residues after the codon 391) color-coding of the C-terminal domain gives a schematic representation of where these sequences differ to GFAPα. The single-letter amino acid code for tail domain of the WT GFAP (GFAPα) is also given and the disease-causing mutations studied are indicated (red letters). The sequence containing the GA5 epitope is underlined.
