Fig. 7.
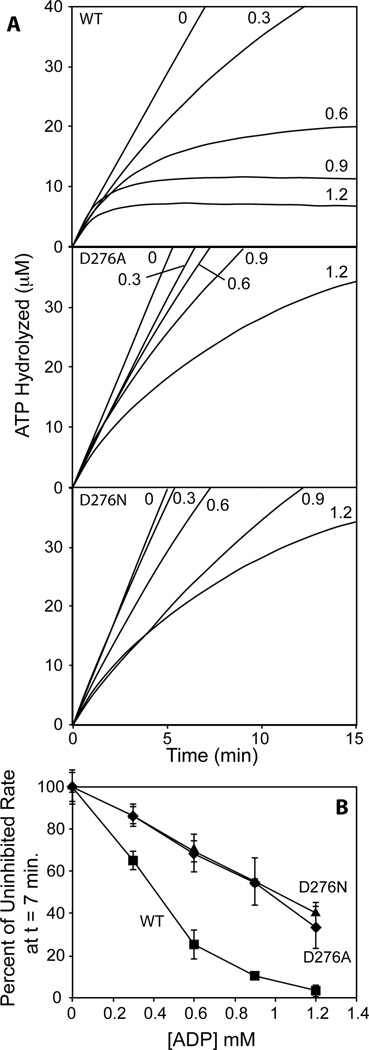
The ATPase activity of RecA D276A and RecA D276N during strand exchange is less inhibited by ADP than that of Wild type RecA. A, Reactions were carried out as described in Experimental Procedures, and ATP hydrolysis was monitored. First, 0.6 µM RecA protein was allowed to hydrolyze ATP in the presence of 1 µM M13mp18 circular ssDNA, 1.5 mM ATP, and 0.1 µM SSB for five minutes, and then 2 µM homologous M13mp18 linear dsDNA and 0, 0.3, 0.6, 0.9, 1.2, or 1.5 mM ADP were added as a mixture. Graphs are labeled with the variant of RecA protein used in the reactions, and reaction lines are labeled with the concentration of ADP added. Time 0 corresponds to the addition of linear dsDNA and ADP. B, ATP hydrolysis data was fit with a polynomial curve and this fit was differentiated at time 7 minutes after the addition of linear dsDNA and ADP to determine the rate of hydrolysis of ATP at that time. Values from three independent experiments were averaged, and then expressed as the percentage of the rate at 7 minutes in the reaction in which no ADP was added. Vertical error bars display propogated standard deviation. Wild type RecA points are shown as squares, RecA D276A points are shown as diamonds, and RecA D276N points are shown as triangles
