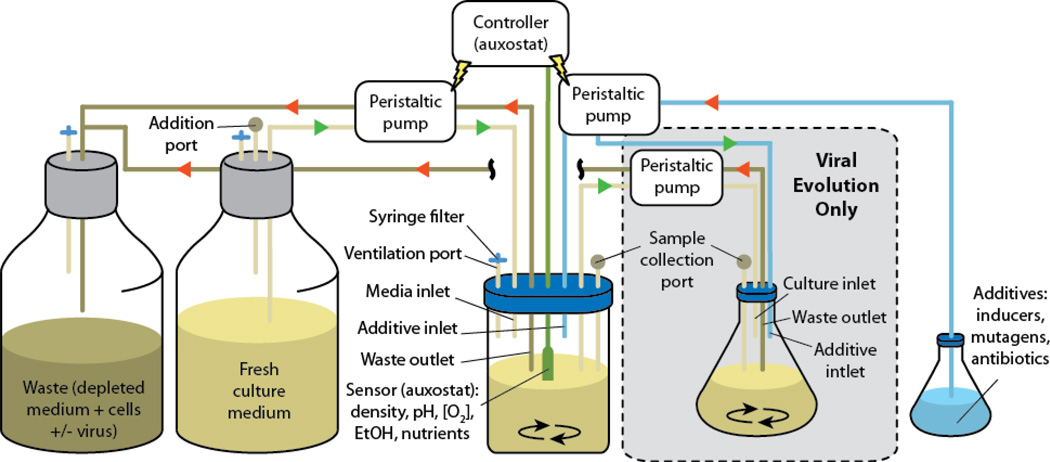
Figure 2. Auxostats and chemostats.
Fresh culture medium is pumped into a pre-sterilized container containing the microorganism of interest. Medium with cells is pumped out of the culture container. The rates of medium input and output are held constant in a chemostat system, and the growth rate is regulated by the composition of the medium. In an auxostat system, the medium flow rates are dynamically regulated by a controller in response to measurements made in the growing culture, which correspond directly (turbidity meter) or indirectly (other sensors) to the culture density. In schemes for viral continuous evolution, the auxostat or chemostat culture is pumped into a new vessel where the virus of interest is supplied (cellstat). Both cultures can be supplemented with additives supplied through a dedicated inlet. Selection stringency can be regulated by varying flow rates, changing temperature, or adding compounds to the auxostat, chemostat or cellstat. The depleted medium, cells and virus are pumped to a waste container.