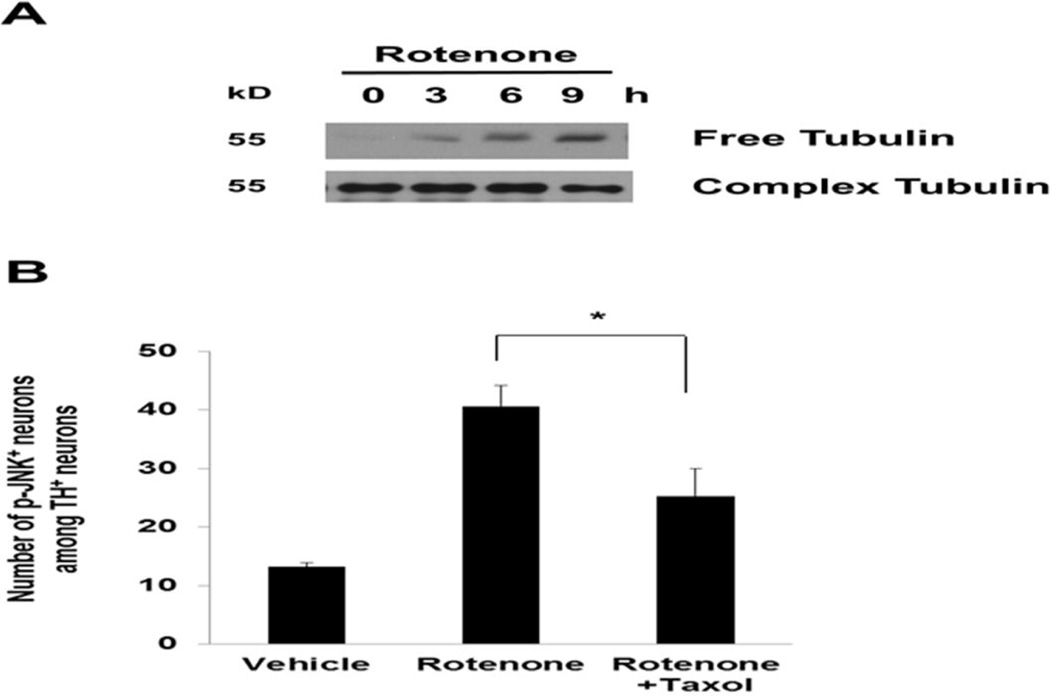
Fig. 5. Rotenone-induced microtubule de-polymerization activates JNK.
(A) Accumulation of free tubulin after rotenone treatment, indicative of microtubule destabilization. E14 mesencephalic cultures were treated with 5 nM rotenone for 0, 3, 6, or 9 h. Cell lysates were prepared for Western analysis. (B) Taxol attenuates rotenone-induced JNK phosphorylation, an indicator of JNK activation. E14 mesencephalic cultures were co-treated with 5 nM rotenone and 10 nM taxol and for 8 h. Immunostaining was performed using anti-TH and anti-phospho-JNK (p-JNK) antibodies.