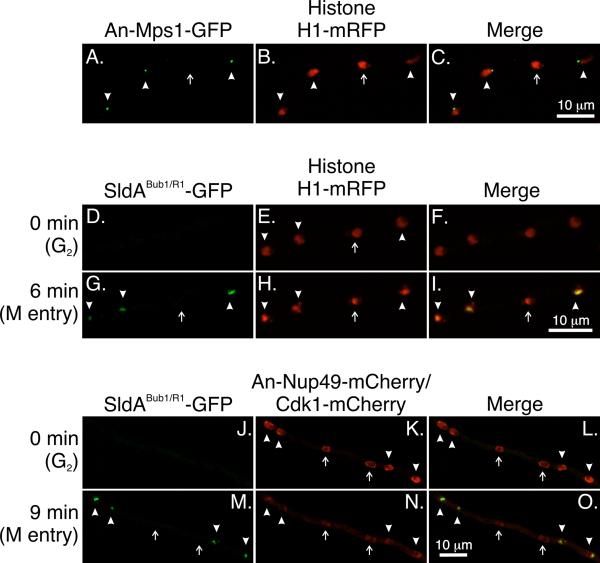
Fig. 7.
An-Mps1 and SldABub1/R1 fail to accumulate in a subset of nuclei at restrictive temperatures in strains carrying mipAD159. Images are maximum intensity projections from Z-series stacks captured at at 25°C. The Z-series stacks captured all of the nuclei in their entirety so the absence of fluorescence is not due to a portion of a nucleus simply being beyond the limits of the Z-series stack. A-C: Four nuclei are shown. An-Mps1 fluorescence is visible at the SPBs of three nuclei (arrowheads) but not the fourth (arrow). D-I: SldABub1/R1 does not accumulate in a subset of nuclei. Images were from a time-lapse data set with stacks captured at 3 min intervals. At T = 0 SldABub1/R1 -GFP is not detectable in any nuclei. At T = 6 min it is present in three of four nuclei (arrowheads) but not in one nucleus (arrow). J-O: SldABub1/R1 does not accumulate in Cdk1− nuclei. At T = 0 SldABub1/R1 is not present in any nuclei. All nuclei show nuclear periphery fluorescence due to An-Nup49-mCherry. Cdk1+ nuclei (arrowheads) show additional fluorescence at the SPBs and Cdk1 is present in the nucleoplasm except for the nucleolar region (visible as a small clear area). Two nuclei are Cdk1− (arrows). They do not show SPB fluorescence and the nucleoplasm is clear. At T = 9 min SldABub1/R1 has accumulated in the Cdk1+ nuclei (arrowheads) but not in the Cdk1− nuclei (arrows). At this time point, the nuclear pores are partially disassembling and the An-Nup49-mCherry fluorescence is, consequently, fainter than at T = 0. Also at this time, Cdk1 leaves Cdk1+ nuclei as previously reported (Nayak et al., 2010) so there is little difference in nuclear Cdk1 levels between Cdk1+ and Cdk1− nuclei. Most fluorescence in the nuclei is due to out of focal plane fluorescence from An-Nup49-mCherry and cytoplasmic Cdk1-mCherry.