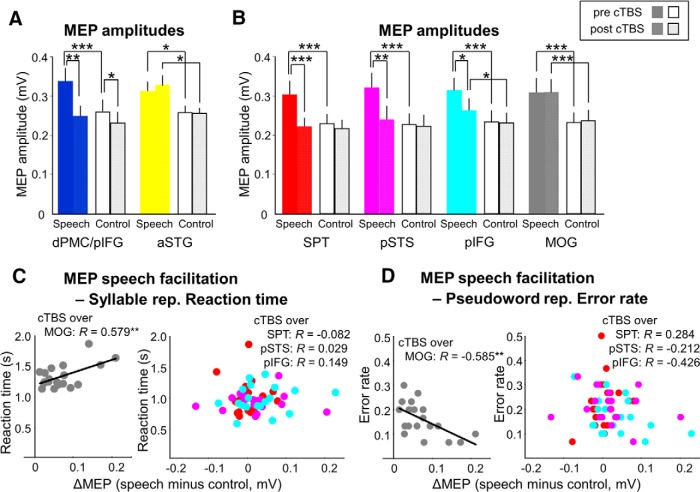
Figure 7.
cTBS effects on speech-related modulation of articulatory M1 excitability and correlation analyses with behavioral performance. A, In nine control subjects, the double knock-out of dPMC and pIFG disrupted speech-related MEP facilitation, whereas cTBS of aSTG in the ventral stream did not (speech: passive listening to German sentences; control: listening to white noise). B, In 19 participants, the speech-related MEP facilitation was disrupted after cTBS of the left SPT, pSTS, and pIFG, but not after cTBS of MOG. C, The speech-related MEP facilitation after cTBS of MOG correlated positively with reaction time during correct syllable repetition, whereas cTBS of SPT, pSTS, and pIFG disrupted this relationship. D, The speech-related MEP facilitation after cTBS of MOG correlated negatively with error rates of pseudoword repetition, whereas cTBS of SPT, pSTS, and pIFG decorrelated the electrophysiological measure from behavior. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01. ***p < 0.001. Error bars indicate SEM.