Figure 4.
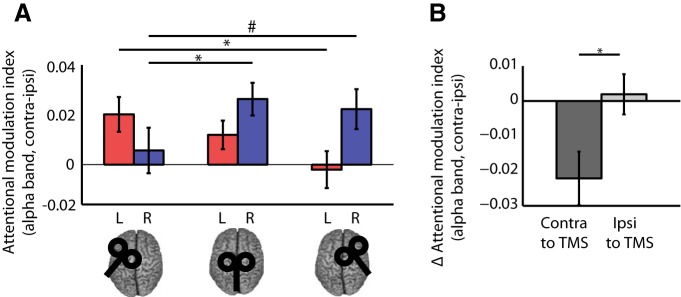
Alpha modulation from the sensor ROI data. A, Attentional modulation index (AMI) for all TMS sites and sensor ROIs. The AMI is defined as (attention contra − ipsi)/(average over all attention and TMS conditions), resulting in positive values for appropriate modulation for both hemispheres, as shown in the vertex condition. Statistical analysis revealed an interaction of TMS site and hemisphere (sensor ROI), as well as conditional main effects of TMS site for each hemisphere analyzed separately. Stimulation of left or right FEFs disrupted alpha modulation in parieto-occipital sensors in the contralateral hemisphere. Significant (p < 0.05) post hoc comparisons are indicated by asterisks, trends (p < 0.1) are indicated by hashes. B, Change in alpha modulation at sensor sites in the hemisphere contralateral and ipsilateral to TMS. The change (Δ) in AMI was calculated by subtracting the modulation in each ROI in each TMS session from the corresponding data in the control (vertex) session. Δ AMI scores were then averaged across ROIs separately for the hemisphere ipsilateral or contralateral to the stimulation (i.e., left ROI following left FEF TMS and right ROI following right FEF TMS and vice versa, respectively). Statistical analyses confirmed a stronger effect of FEF TMS on alpha modulation in the hemisphere contralateral versus ipsilateral to the stimulation (p < 0.05).
