Fig. 2.
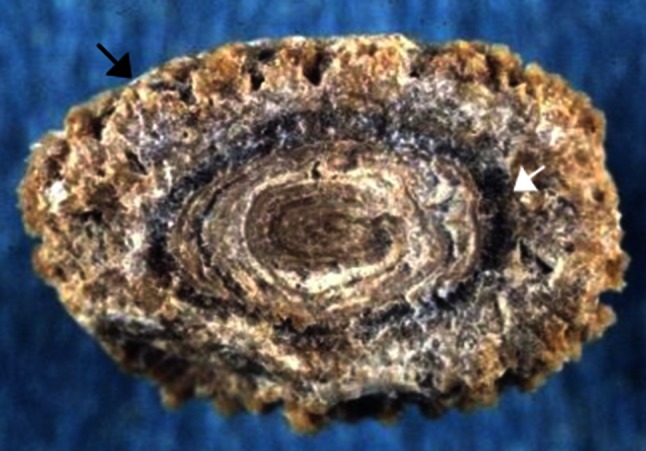
Kidney stone from a child aged 9 years old. Examination of the stone section shows a mixed stone initiated by crystallization of ammonium hydrogen urate as a result of chronic diarrhea related to bowel infection while the child ate a vegetable diet providing insufficient protein and phosphorus intake. Ammonium urate was secondly covered by whewellite (white arrow) as a consequence of oxalate-rich diet and low water intake. The further coverage by a mixture of weddellite and carbapatite (black arrow) was the consequence of changes in life style resulting in an easy access to dairy products. The child developed hypercalciuria of dietary origin
