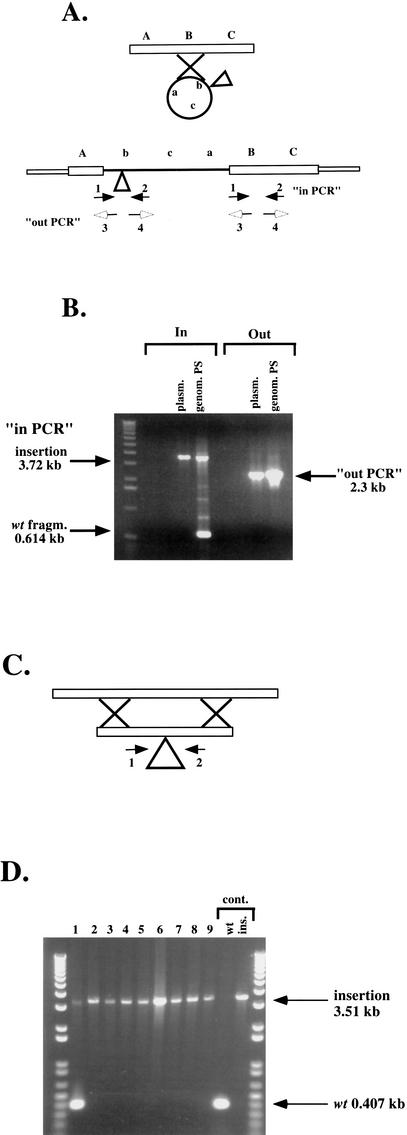
Figure 2.
Two of the pathways of homologous recombination after transformation of linearized mutant fosmids. (A) Class 2 (partially stable, PS) transformants: A linearized genomic fragment containing a transposon insertion can recircularize before, or at the time of, homologous recombination, generating a duplication of the region as indicated. Primers 1 and 2 are oriented toward, and primers 3 and 4 oriented away from the Tn7 insertion. (B) Result of PCR amplification of genomic DNA from one Class 2 transformant. (genom.PS lane) Template DNA for PCR was genomic DNA; (plasm. lane) template DNA for PCR was pIC14. (C) Class 3 (stable, S) transformants: allele replacement. A linearized genomic fragment containing a transposon insertion recombines by double crossover and replaces the genomic locus. (D) Result of PCR amplification of genomic DNA from nine Class 3 (S) transformants. (Lane 1) Genomic DNA from a nonhomologous recombinant was used for the PCR and bands for both the wild type and Tn7-disrupted copies are amplified. (Lanes 2–9) Results for homologous recombinants. Controls: (wt) Cg14 genomic DNA was used as template for the PCR; (ins.) pIC14 was used as template.