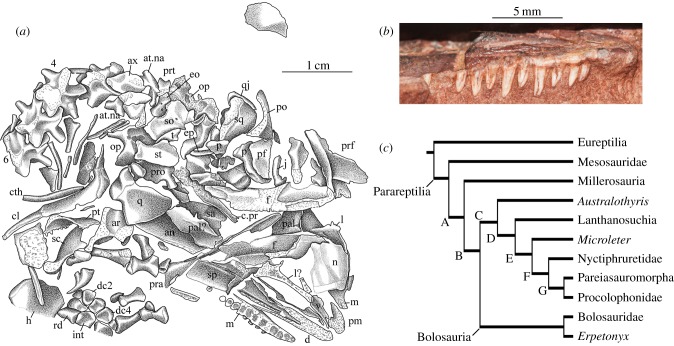
Figure 2.
Erpetonyx arsenaultorum n. gen. et sp., ROM 55402, holotype. (a) Interpretive drawing of skull. (b) Photograph of right maxillary dentition in lateral view. (c) Results of phylogenetic analysis; tree length = 557, consistency index (CI) = 0.3429, CI excluding informative characters = 0.3405, retention index = 0.6355, rescaled CI = 0.2179. Bootstrap/Bremer support values: Bolosauria: 39/3; Parareptilia: 13/1; clade A: 33/2; clade B (Procolophonomorpha): 32/2; clade C: 11/2; clade D (Ankyramorpha): 12/2; clade E: 19/2; clade F: 44/1; clade G: 15/1. Bolosauria is diagnosed by the following unambiguous synapomorphies: postparietal small (character 9, state 1); transverse flange of pterygoid dentition present (character 70, state 1); anterior caudal ribs elongate and extend posteriorly to end of next vertebra (character 132, state 0); greater trochanter of femur present (character 156, state 1); maxillary tooth positions number 15 or fewer (character 167, state 0). Anatomical abbreviations: an, angular; ar, articular; at.na, atlantal neural arch; ax, axis; cl, clavicle; cth, cleithrum; d, dentary; dc2, distal carpal 2; dc4, distal carpal 4; c.pr, cultriform process of parasphenoid; eo, exoccipital; ep, epipterygoid; f, frontal; int, intermedium; j, jugal; l, lacrimal; m, maxilla; n, nasal; op, opisthotic; p, parietal; pal, palatine; pf, postfrontal; pm, premaxilla; po, postorbital; pra, prearticular; pro, prootic; prf, prefrontal; prt, proatlas; pt, pterygoid; q, quadrate; qj, quadratojugal; rd, radiale; sa, surangular; sc, scapula; so, supraoccipital; sp, splenial; sq, squamosal; st, supratemporal; t, tabular; v, vomer. Arabic numerals identify cervical vertebrae. (Online version in colour.)