Figure 1.
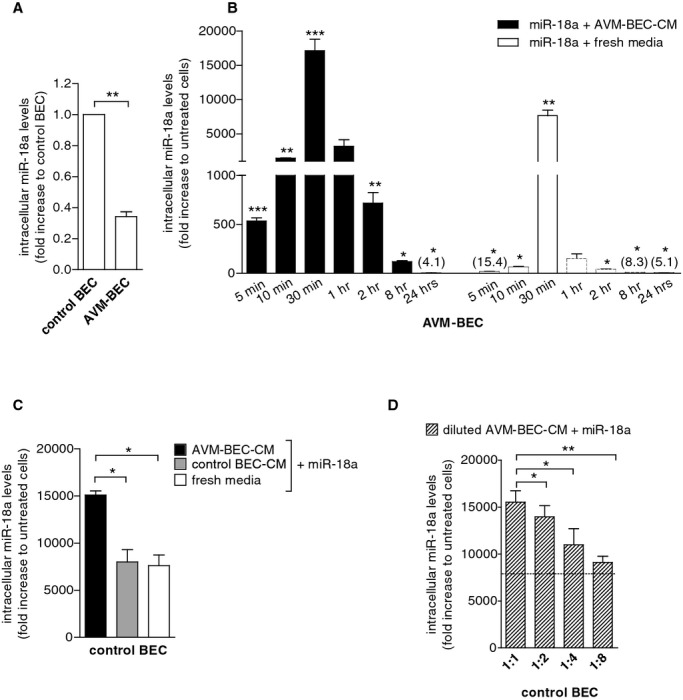
AVM‐BEC‐conditioned media (AVM‐BEC‐CM) potentiates miR‐18a internalization. A, AVM‐BEC and control BEC were analyzed for intracellular miR‐18a levels using qPCR. Control BEC were used as baseline (n=3; ***P<0.001; paired t test). B, miR‐18a (40 nmol/L) in combination with AVM‐BEC‐CM (black bars) or fresh culture media (white bars) was added to AVM‐BEC and tested for intracellular miR‐18a after 5, 10, 30 minutes (n=4), 1, 2, 8 and 24 hours (n=3). AVM‐BEC‐CM enhanced miR‐18a entry up to 30 minutes (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001; paired t test). C, Control BEC were treated with miR‐18a (40 nmol/L) in combination with AVM‐BEC‐CM (black bar), control BEC‐CM (gray bar) or fresh media (white bar). Intracellular miR‐18a was analyzed (qPCR) after 30 minutes incubation; AVM‐BEC‐CM potentiated miR‐18a internalization by control BEC (n=3; *P<0.05; paired t test). D, Control BEC were treated with miR‐18a (40 nmol/L) and in the presence of serial diluted AVM‐BEC‐CM (diagonal line bars), demonstrating that progressively diluted AVM‐BEC‐CM loses its ability to enhance miR‐18a internalization (n=3, *P<0.05, **P<0.01; paired t test). Dotted line represents miR‐18a uptake by control BEC in the presence of fresh media. Data are presented as mean±standard error of the mean (SEM). Each human specimen‐derived cell culture represents a unit of analysis (n). AVM indicates arteriovenous malformation; BEC, brain endothelial cells; CM, conditioned media; qPCR, quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction.
