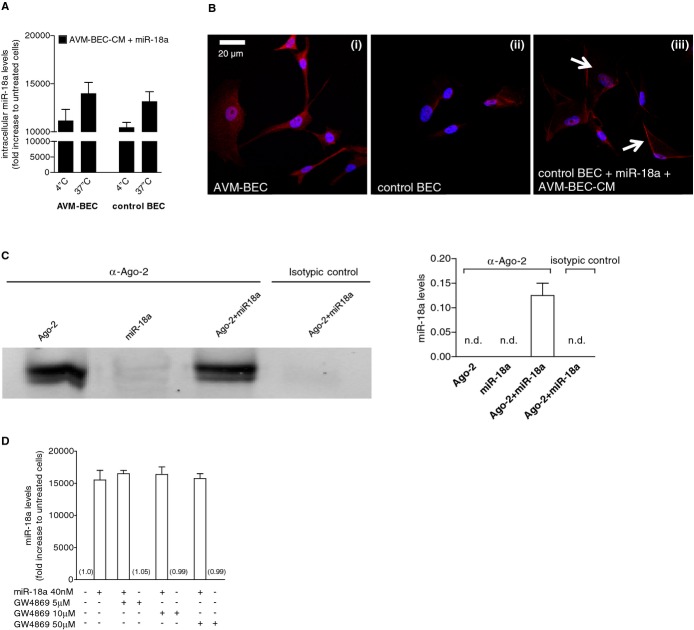
Figure 4.
Facilitated transport is involved in miR‐18a delivery. A, AVM‐BEC and control BEC were treated with AVM‐BEC‐CM plus miR‐18a (40 nmol/L) at 4°C and 37°C for 30 minutes. Intracellular miR‐18a was measured using qPCR as described previously, showing that at 4°C miRNA entry was only minimally compromised (n=3). B, The distribution of Ago‐2 (red) was identified using immunocytochemistry. At 4°C untreated AVM‐BEC expressed high levels of intracellular Ago‐2 (i) compared to untreated control BEC (ii). When control BEC were treated with AVM‐BEC‐CM plus miR‐18a at 4°C, Ago‐2 staining was apparent and associated with the cell membrane (iii; white arrows) (n=3). Blue staining denotes nuclear staining. C, The formation of a ribonucleoprotein complex between Ago‐2 and miR‐18a was determined by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting (left panel) and qPCR (right panel). Ago‐2 was detected only in the 2 fractions in contact with anti‐Ago‐2, as expected. Only the fraction with both Ago‐2 and miR‐18, but not miR‐18a alone, led to the detection of miR‐18a by qPCR. Rabbit IgG served as the isotypic control. D, GW4869 (10 to 50 μmol/L), a specific inhibitor of N‐Smase‐2 (neutral sphingomyelinase‐2) did not interfere with miR‐18a uptake in AVM‐BEC. Data are presented as mean±standard error of the mean (SEM). Each human specimen‐derived cell culture represents a unit of analysis (n). AVM indicates arteriovenous malformation; Ago‐2, Argonaute‐2; BEC, brain endothelial cells; CM, conditioned media; qPCR, quantitative real‐time polymerase chain reaction.