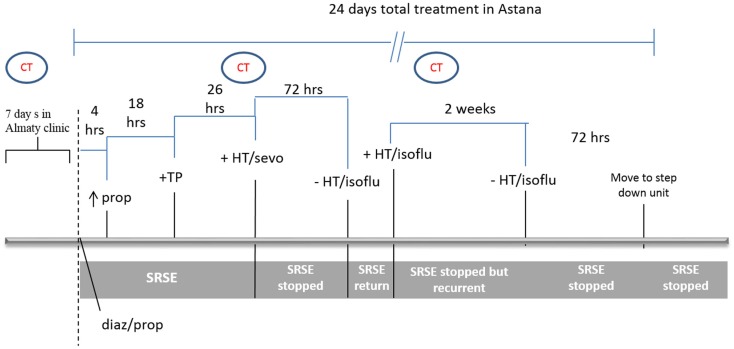
Figure 1.
Clinical course and treatment timeline. Initial therapy included diazepam (diaz) 0.15 mg/kg, and propofol (prop) 0.027 mg/kg/min. Four hours later, the dose of propofol was increased to 0.09 mg/kg/min. Eighteen hours later, prop was exchanged for sodium thiopental (TP). Twenty-six hours later, general anesthesia was induced with isoflurane (isoflu) and HT initiated. After seizures were dormant for 72 h, the patient was removed from isoflurane and rewarmed, at which point, seizures returned. Isoflurane anesthesia and HT were reinitiated and continued for 2 weeks, during which the patient was stable without super-refractory status epilepticus (SRSE). Attempts to withdraw from treatment were unsuccessful over these 2 weeks. The patient was then gradually removed from isoflurane and HT, remained seizure-free for 72 h and was then released from the ICU.