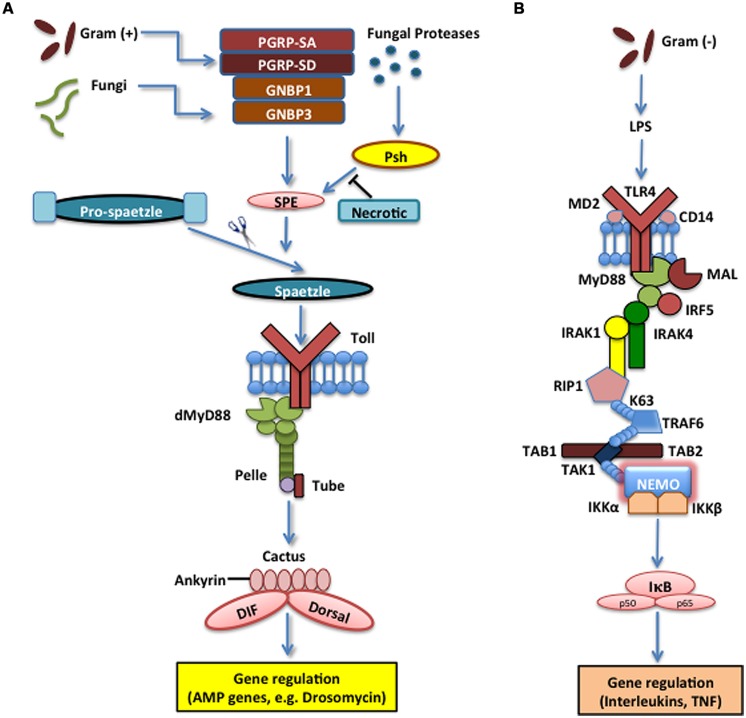
FIGURE 1.
The Toll pathway in the fruit fly and the Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 pathway in the mouse. (A) The Toll pathway in Drosophila melanogaster mainly detects fungi and Gram-positive bacteria. The Toll receptor is triggered upon binding by the cleaved form of the cytokine Spaetzle, which is processed by Spaetzle-processing enzyme (SPE) and other serine proteases that are regulated by the pathogen recognition peptidoglycan recognition proteins (PGRP) PGRP-SA, PGRP-SD, GNBP1, and GNBP3. Serine protease Persephone (Psh) is activated by virulence factors secreted by entomopathogenic fungi and is regulated by Necrotic, a Psh inhibitor. Toll receptor activation results in the recruitment of adaptor proteins in the cytoplasm including myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (dMyD88), Tube, and Pelle, which promotes signaling to Cactus and its ankyrin-repeat domains. Cactus is normally bound to the Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-κB) transcription factors Dorsal-related Immunity Factor (DIF) and Dorsal, but upon activation of the signaling pathway, it is phosophorylated, dissociated from DIF or Dorsal and degraded. These signaling events result in the nuclear translocation of DIF or Dorsal that induce the transcriptional upregulation of antimicrobial peptide (AMP) genes, such as Drosomycin. (B) TLR4 receptor in Mus musculus functions together with Lymphocyte Antigen 96 (MD2) and Cluster of Differentiation 14 (CD14) to detect lipopolysaccharides (LPS) from Gram-negative bacteria. MyD88 is recruited with Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases 1 and 4 (IRAK1, IRAK4), receptor-interacting protein 1 (RIP1) and Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) receptor associated factor 6 (TRAF6). The latter ubiquitinates itself to recruit Transforming Growth Factor beta (TGF-β) activated kinase 1 (TAK1) and TAK1-associated binding proteins 1 and 2 (TAB1 and TAB2), which result in the activation of the IκB kinase (IKK) complex that phosphorylates the Inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB). This leads to the release of NF-κB that translocates to the nucleus and initiates the transcriptional induction of inflammatory and immune response related genes.