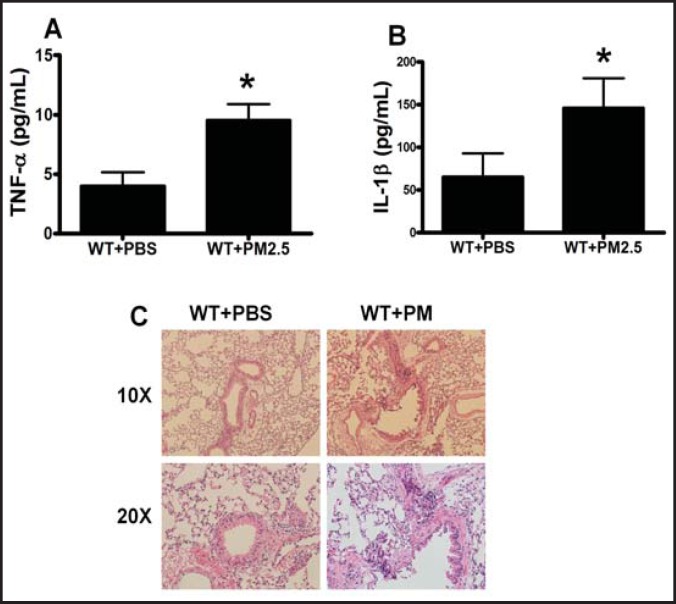
Fig. 2.
PM increased the levels of serum proinflammatory cytokines and induced lung inflammation infiltration. The murine serum was prepared for proinflammatory cytokine TNF-α and IL-1β measurements, and lung was collected for inflammation infiltration analysis after exposure in C57BL/6 mice with PM or PBS for 1 month. There was a significant increase in both TNF-α (A) and IL-1β (B) in the serum in the mice with PM exposure compared with the PBS control. The inflammation level was significantly increased in murine lung with PM exposure. WT+PBS: C57BL/6 mice with PBS treatment; WT+ PM: C57BL/6 mice with PM exposure. * WT+ PM vs WT+PBS P<0.01, n=8.