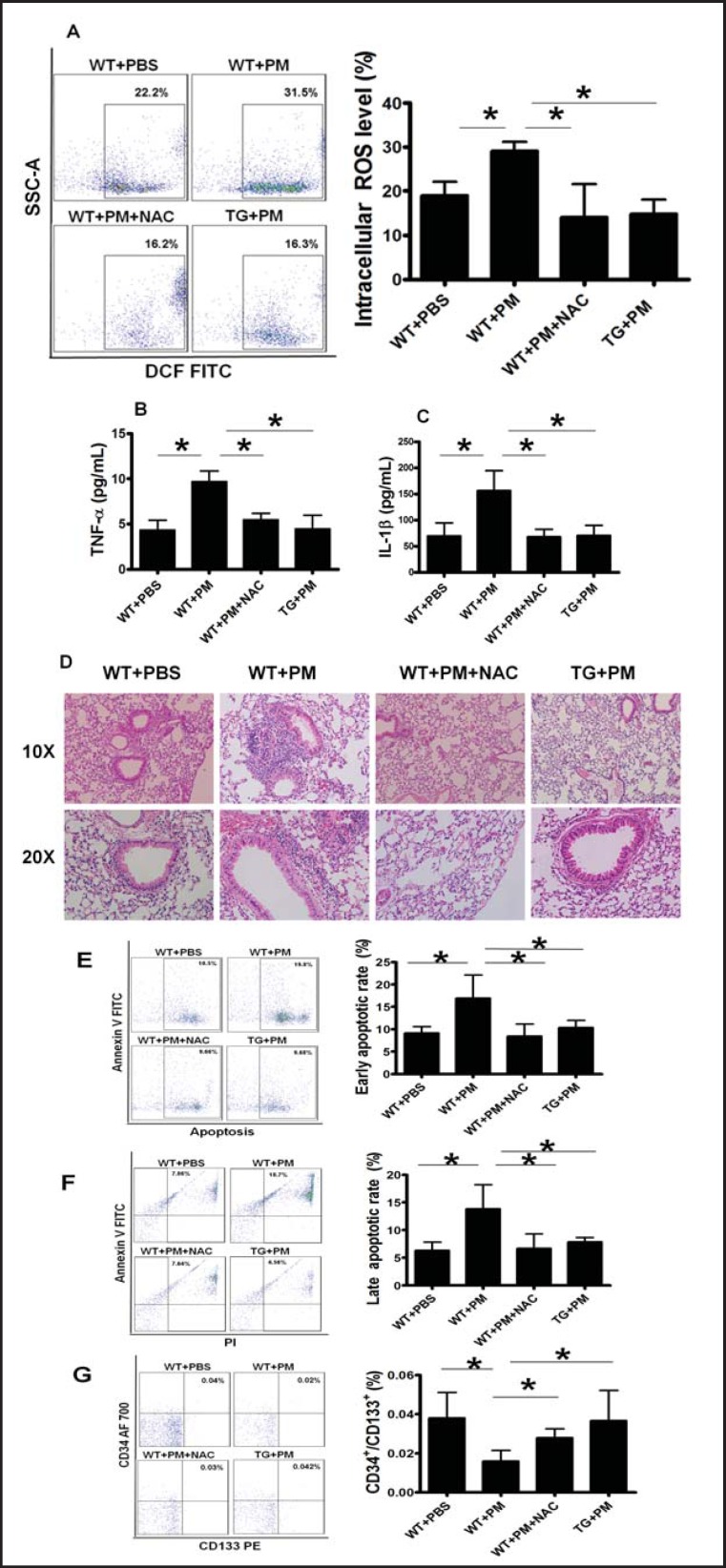
Fig. 4.
NAC treatment or AON overexpression decreased ROS production and reversed the detrimental effects of PM. (A) Increased blood intracellular ROS production was effectively blocked by NAC treatment or AON overexpression in the mice exposed with PM. The murine lung inflammation was much lower in TG mouse and WT mouse with NAC treatment than the WT mouse with PM exposure. Increased level of serum proinflammatory cytokine TNF-α (B) and IL-lβ (C) as well as lung inflammation infiltration (D) was significantly decreased by NAC treatment or AON overexpression in the mice exposed with PM. Increased early apoptotic (E) and late apoptotic (F) rate were effectively reversed by NAC treatment or AON overexpression in the mice exposed with PM. (G) Decreased circulating EPC level was completely restored by NAC treatment or AON overexpression in the mice exposed with PM. WT+PBS: C57BL/6 mice with PBS treatment; WT+ PM: C57BL/6 mice with PM exposure; WT+ PM+NAC: C57BL/6 mice with PM exposure and NAC treatment; TG+ PM: TG mouse with PM exposure. * WT+ PM vs WT+PBS or WT+ PM+NAC or TG+PM P<0.01, n=8.