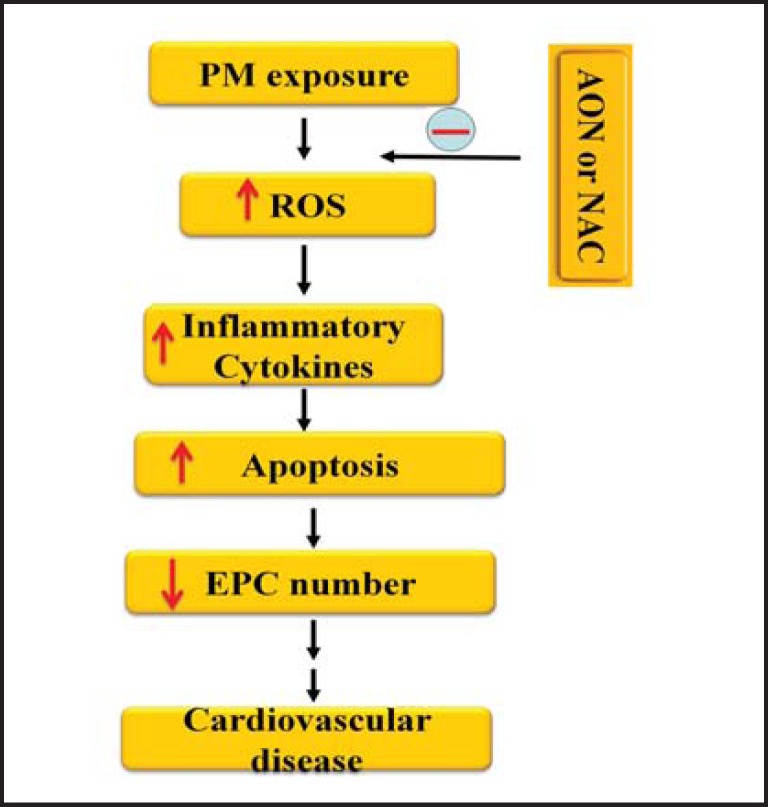
Fig. 5.
Illustration of possible mechanisms for decreased number of circulating EPCs in the mice with PM exposure. PM exposure increased blood intracellular ROS production and inflammatory cytokine level. Blood cell apoptotic rate was then significantly increased, and the circulating EPC number was notably decreased which could contribute to the development of atherosclerosis and other cardiovascular diseases. NAC or AON attenuated the PM-induced ROS formation and decreased serum inflammatory cytokine level and apoptotic rate of EPCs. The circulating EPC number was significantly recovered with NAC treatment or AON overexpression in the mice exposed to PM. PM: particulate matter; ROS: reactive oxygen species; EPC: endothelial progenitor cell; AON: antioxidant enzyme network; NAC: N-acetylcy-steine; ↑: increase; ↓: decrease.