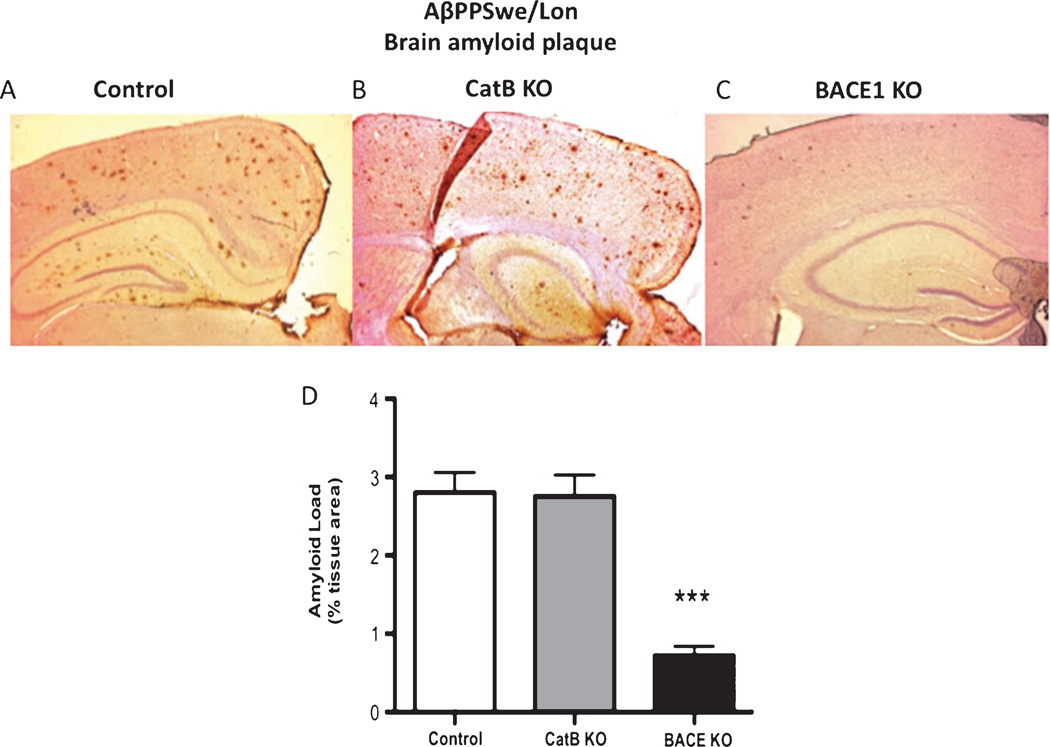
Fig. 8.
Knockout of the BACE1 gene, but not CatB, in AβPPSwe/Lon mice reduces brain amyloid plaque load. Amyloid plaque load was determined by immunohistochemistry and image analysis of brain sections from AβPPSwe/Lon (control), AβPPSwe/Lon × CatB KO (CatB KO), and AβPPSwe/Lon × BACE1 KO (BACE1 KO) as shown in A, B, and C, respectively. Arrows indicate amyloid plaque deposits (A, C). Qualitative analyses of the areas of plaque load were conducted (D). AβPPSwe/Lon, AβPPSwe/Lon × CatB KO, and AβPPSwe/Lon × BACE1 KO mice had mean percent amyloid plaque loads of 2.8%, 2.8%, and 0.7% of brain plaque area, respectively (D). Values in D are expressed as x ± s.e.m., and n = 10. ***Statistically significant (p < 0.05).