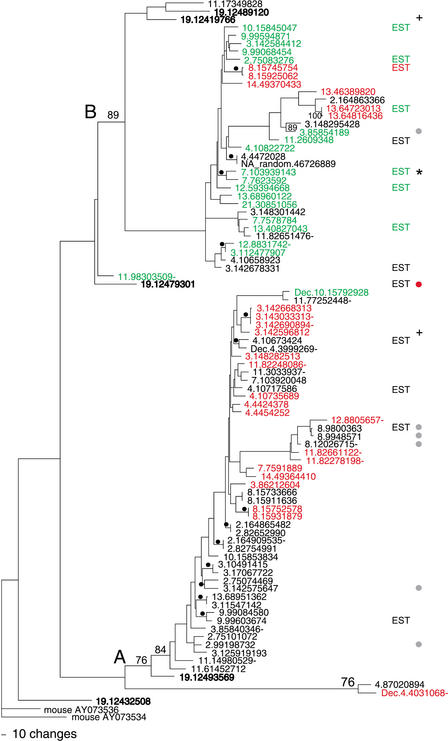
Figure 1.
A parsimony tree of the 88 7E nucleotide sequences. The two major clades of the tree are labeled (A) and (B). Bootstrap values (% of 1000 iterations) are indicated when >75% on the major branches and marked with black dots when ≥85% on the minor banches. The 7E genes are labeled by their position in the UCSC August 2001 assembly of human draft sequence (see Methods); Supplementary Table A gives the corresponding names assigned to the genes by Glusman et al. (2000a) and/or in HORDE. We also included in our set of 88 the sequences for three 7E genes that are found in two finished BACs (AL360083 and AC073648) included in later assemblies (these names of these genes carry the prefix Dec). Genes in bold type are those found in the ancestral locus on chromosome 19. Genes with names in red contain a common substitution resulting in a stop codon in TM6, and those in green contain a common frame shift leading to a stop codon in TM3. The gene marked by a red dot encodes an ORF containing seven TM regions and also encodes a methionine at the beginning of the first predicted extracellular region. Genes marked by a gray dot have ORFs that are predicted to encode six TM regions. Genes marked + have a Ks/Ka value ≥5 on average when compared to 75% of the other 7E genes. “EST” designates genes that match (≥98%) human ESTs. “EST*” designates a gene that matches spliced ESTs. Gene names followed by a dash are not part of 7E SDs.