Figure 7. Acute Mn exposure alters the SDS-solubility of aggregates in a polyglutamine model.
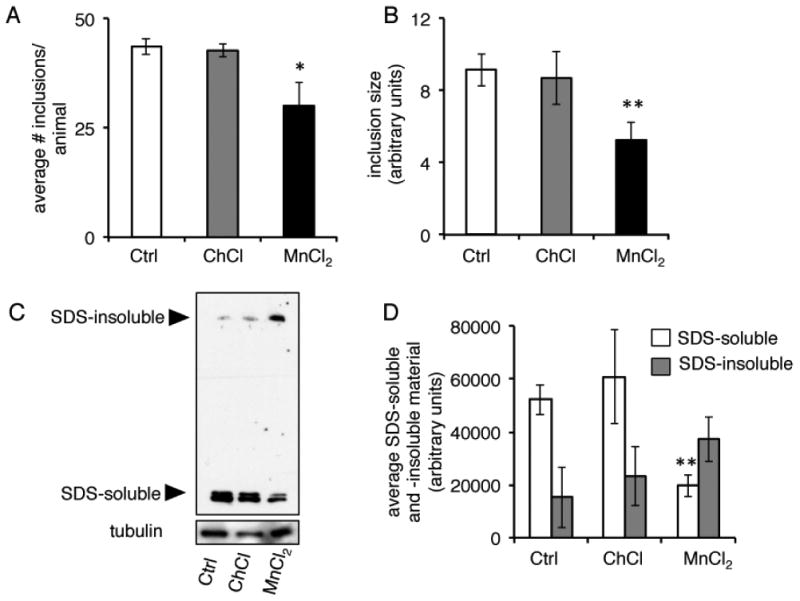
A, Quantification of number of YFP inclusions in day 1 adult worms expressing a 40 polyglutamine repeat tagged to YFP in their body wall muscle (AM141 [rmIs133(P(unc-54) Q40::YFP)]) after 24 hour treatment with water (Ctrl), 20 mM ChCl, or 20 mM MnCl2 (*=p<0.03, Student's t-test). B, Quantification of relative size of YFP inclusions in day 1 animals after 24 hour treatment with water (Ctrl), 20 mM ChCl, or 20 mM MnCl2 (**p=<0.01, Student's t-test). C, Immunoblots of protein extracts from day 1 animals after 24 hour treatment with water (Ctrl), 20 mM ChCl, or 20 mM MnCl2. Aggregates were separated into SDS-soluble or SDS-insoluble fractions (higher molecular weights). D, Quantification of SDS-soluble and -insoluble material from immunoblots (n=3, **p=<0.01, Student's t-test).
