Figure 8. Modes of Mn toxicity.
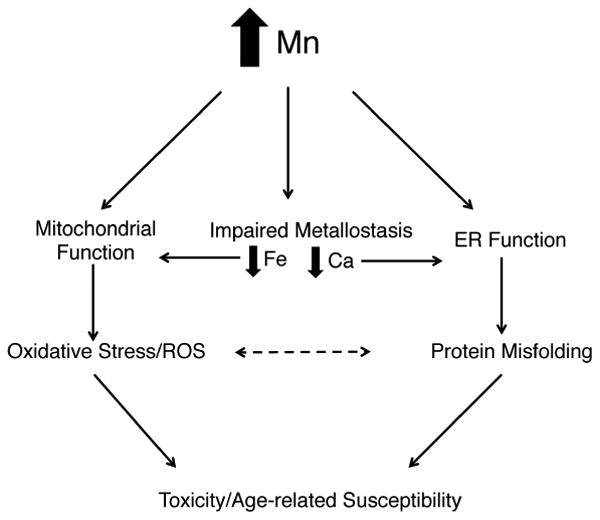
Schematic of potential avenues of Mn-toxicity. Mn directly affects mitochondrial function by disrupting mitochondria complex I and depleting mitochondrial ATP stores, which activates the mitochondrial stress response and stimulates ROS production, leading to toxicity and cell death. Mn can also directly perturb protein misfolding, which activates the ER stress response and leads to toxicity and cell death. Mn alters Fe homeostasis, which can lead to mitochondrial dysfunction and increase its participation in the Fenton reaction and ROS production. Mn alters Ca homeostasis, which can lead to ER dysfunction and exacerbates protein misfolding. Oxidative stress may exacerbate protein misfolding and vice versa. All pathways can eventually contribute to toxicity and cell death.
