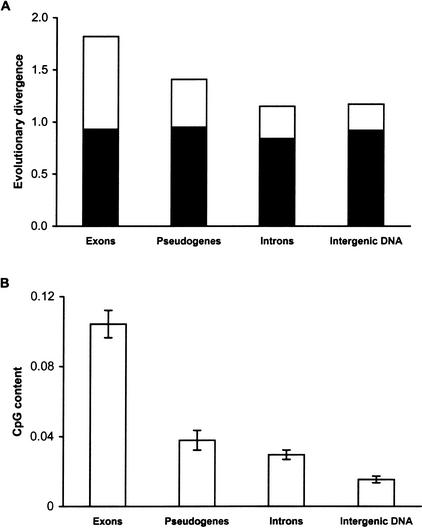
Figure 1.
(A) Evolutionary divergence per 100 sites and (B) CpG contents of synonymous sites in exons, pseudogenes, introns, and intergenic DNA for the human–chimpanzee comparison. The mean and the standard error estimates shown were obtained from 81 protein coding genes, 19 pseudogenes, introns of 48 genes, and four intergenic blocks. In (A), the total height of each column (including black and open bars) corresponds to the overall evolutionary divergence. The black portion in each column depicts divergence with CpG sites excluded, and therefore, the open bars show the contribution of mutations at CpG sites to the overall divergence. In (B), the CpG content is the proportion of sites involved in the CpG dinucleotide configuration. For noncoding DNA, all sites were included for the estimation of CpG content and evolutionary divergence, whereas for exons only the fourfold-degenerate sites were included (see Methods).