Figure 3.
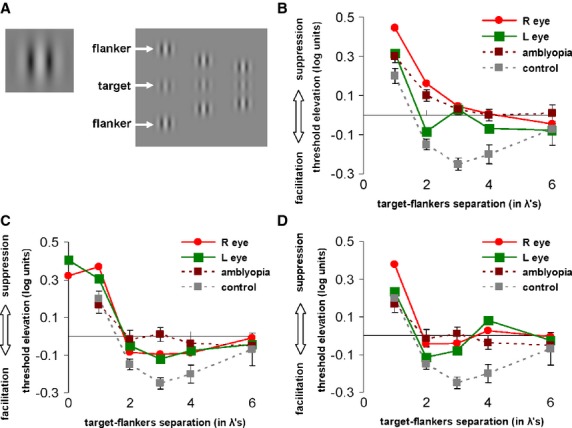
Lateral interactions before and after LG's training. (A) Collinear lateral interactions stimuli examples, in which contrast detection threshold of a single flashed Gabor patch at fixation (on left) is measured against detection threshold of displays with lateral high contrast collinear flankers (appearing above and below target) at various distances (on right, three columnar examples of different distances). (B–D) The x-axes denote target-flankers separation in wavelengths (λ), y-axes denote the contrast detection threshold difference (single target vs. with flankers) in log units. (B) Before training LG's lateral interactions were dominated by suppression, especially for 2–3 λ (LG's right (R) and left (L) eyes denoted in red and green, respectively), similar to those found in typical adult amblyopia before training (dashed brick line), and not showing the typical facilitation effect found in normal adults (dashed gray line). (C) After 9 months of training, LG's lateral interactions for λ ≥ 2 (typically showing facilitation in healthy adults controls) showed small but clear facilitation effects, similar to amblyopes following training (dashed brick line), and these effects in LG endured over 4 years post-training (D) for 2–3 λ. The control data presented in panels B, C, and D are the same for all these panels; lateral interactions of typical amblyopes are presented in B, and interactions of amblyopes following training are presented in panels C and D. Error bars indicate SEM.
