Figure 1.
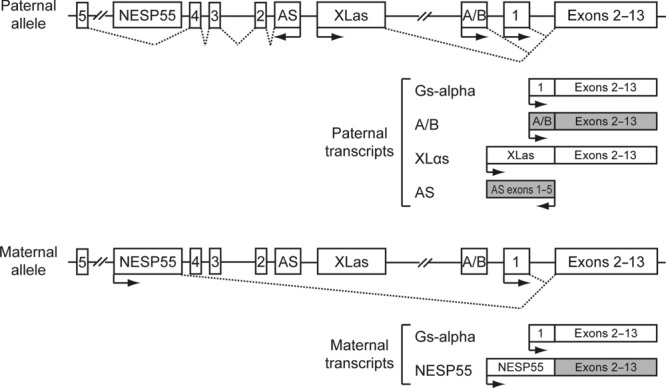
GNAS genomic structure and encoded transcripts. Gs-alpha is encoded by exons 1–13. Other transcripts produced by using alternative first exons that splice on to exons 2–13 are A/B (noncoding), XLαs, and NESP55. An AS noncoding transcript is also produced in the opposite direction using distinct exons. Gs-alpha is transcribed from both the paternal and maternal allele, except in selected tissues, such as renal proximal tubules, thyroid, gonads, and pituitary, in which expression occurs only from the maternal allele. A/B, XLαs, and AS transcripts are paternally expressed, and NESP55 transcripts are maternally expressed, as their promoters are located within DMRs (not shown). Exons are represented by boxes. Arrows indicate the direction of transcription of the different paternal and maternal transcripts. Dashed lines join exons that are spliced to produce the different transcripts. Shaded boxes represent noncoding transcripts.
