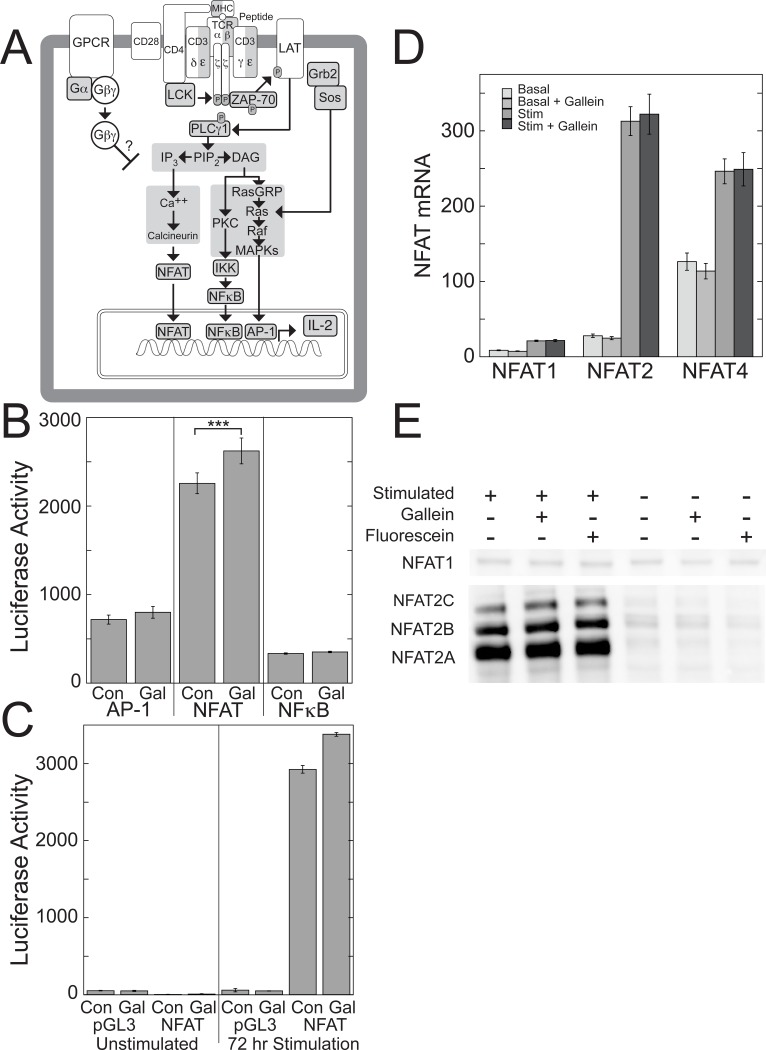
Figure 6. Gallein enhances TCR-stimulated transcriptional activity of NFAT.
(A) Major TCR-stimulated pathways leading to IL-2 transcription that could be inhibited by Gβγ. Interactions between the TCR and peptide-major histocompatibility complex (MHC) lead to recruitment of CD4 and its associated kinase, p56-Lck, which phosphorylates tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic tails of the TCR subunits, leading to recruitment and phosphorylation of the tyrosine kinase, ZAP-70. CD28 costimulation provides an additional signal that is needed for complete T cell activation and regulation of IL-2 production [88]. ZAP-70 and p56-Lck then phosphorylate and activate numerous downstream target proteins, including phospholipase C-γ (PLC-γ), leading to Ras activation, Ca2+ increases, cytoskeletal rearrangements, and ultimately, activation of transcription factors that bind to the IL-2 promoter and increase IL-2 transcription. (B-C) Gallein increases transcriptional activity of NFAT, but not AP-1 or NFκB. Jurkat cells expressing reporter plasmids for AP-1, NFAT, or NFκB, were stimulated with plate-bound anti-CD3 and soluble anti-CD28 in the presence or absence of gallein for three days. (B) Data from TCR-stimulated cells expressing the indicated reporter plasmids represent means ± SE from 7 experiments. ***, p < 0.001. (C) Data from cells expressing empty vector (pGL3) or the NFAT reporter plasmid represent means ± SD from triplicate determinations in a single experiment representative of 7 experiments. (D) Gallein does not affect mRNA levels of NFAT1, NFAT2, or NFAT4. Portions of the Jurkat cells used for the luciferase assays that measured activity at the NFAT ARRE-2 site were used to measure mRNA levels of NFAT1, NFAT2, and NFAT4 by qPCR. Data represent means ± SE from 7 experiments. (E) Gallein does not cause detectable changes in protein levels of NFAT1 or NFAT2. Jurkat cells were stimulated or not with plate-bound anti-CD3 and soluble anti-CD28 in the absence or presence of gallein or fluorescein. The blot of NFAT1 used lysates from cells stimulated for three days and the blot of NFAT2 used lysates from cells stimulated for two days. Similar results were obtained from cells stimulated for one, two, or three days, and in a second independent experiment.