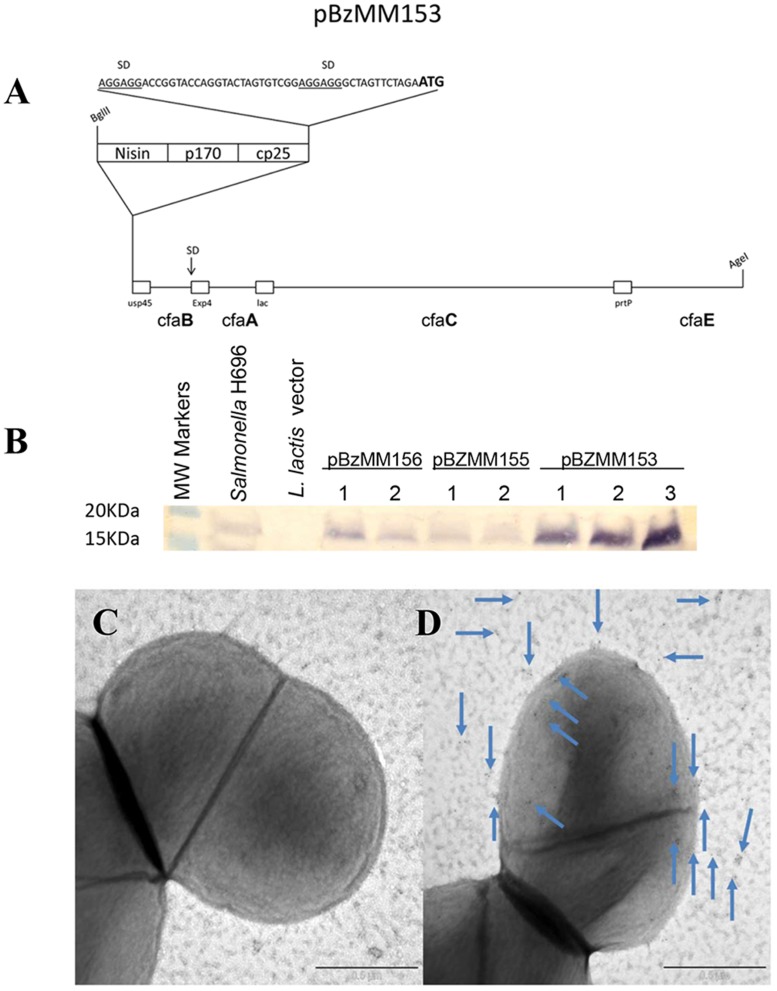
Fig 1. Expression of E. coli cfaI fimbrial operon in Lactococcus lactis.
(A) Schematic map for expression of E. coli cfaI in L. lactis (pBzMM153). The elements of the composite promoter are boxed. Each structural gene is fused in-frame to a different lactococcal secretion signal peptide, and each gene is followed by its own STOP codon. No other functional elements are interspersed except for one Shine-Dalgarno (SD) sequence upstream of a fusion between extracellular (Exp4) protein and cfaA. All (SD) sequences are marked. (B) CFA/I fimbriae expression in L. lactis. Lane1, molecular weight (MW) markers; lane 2, Salmonella-CFA/I (H696) strain; lane 3, L. lactis bearing the empty pMSP3535H3 vector; lanes 4,5, pBzMM156 (nisin-inducible promoter) clones 1 and 2; lanes 6,7, pBzMM155 (p23 promoter) clones 1 and 2; and lanes 8–10, pBzMM153 (synthetic composite promoter) clones 1–3. (C, D) Immunogold staining of (C) L. lactis vector and (D) L. lactis-CFA/I with anti-CFA/I antibody. Arrows point to gold particles on fimbrial structures projecting from the cell wall.