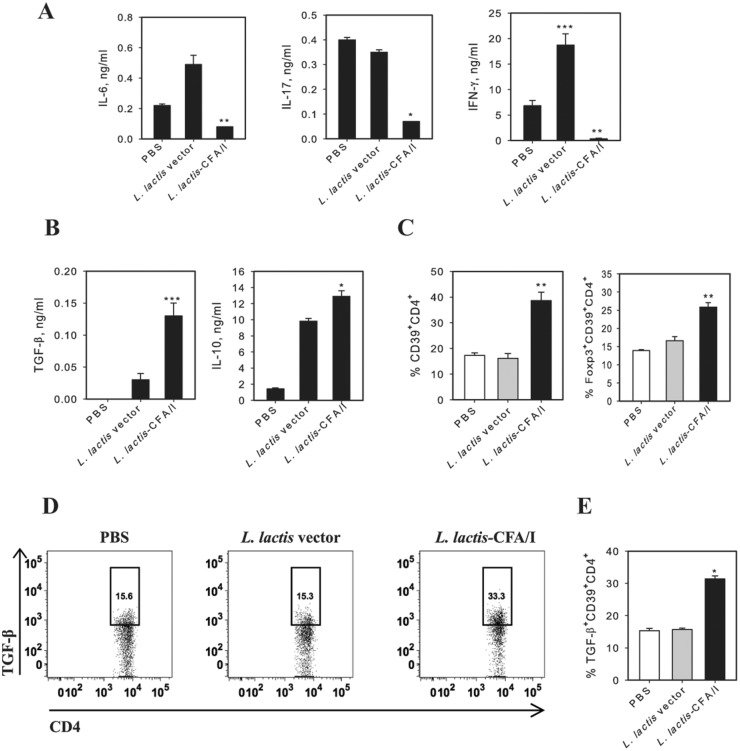
Fig 4. L. lactis-CFA/I reduces CII-specific inflammatory CD4+ T cells with concomitant increases in anti-inflammatory cytokines.
On day 40 post-CIA induction, purified LN CD4+ T cells from each group were restimulated with 50 μg/ml CII for 4 days in presence of syngenic irradiated Ag-presenting cells. (A) L. lactis-CFA/I, not L. lactis vector, suppress IL-6, IL-17, and IFN-γ responses and show elevated (B) TGF-β and IL-10. Depicted are the means ± SD of triplicate cultures as assessed by cytokine-specific ELISA; one of 3 experiments (5 mice/group) is shown. (C) Frequency of CD39+CD4+ T cells in LNs of control and protected mice (5 mice/group). (D, E) Expression of TGF-β for gated LN CD39+CD4+ T cells mice treated with PBS, L. lactis vector, or L. lactis-CFA/I. Representative FACS plots (D) and frequencies of TGF-β+CD39+CD4+ T cells (E) are depicted. For all studies, *p < 0.001, **p < 0.005, and ***p < 0.05 as compared with PBS- and L. lactis vector-treated mice.