Figure 2. REDD1 protein expression in epidermis is tightly regulated and correlates with inhibition of mTOR and autophagy.
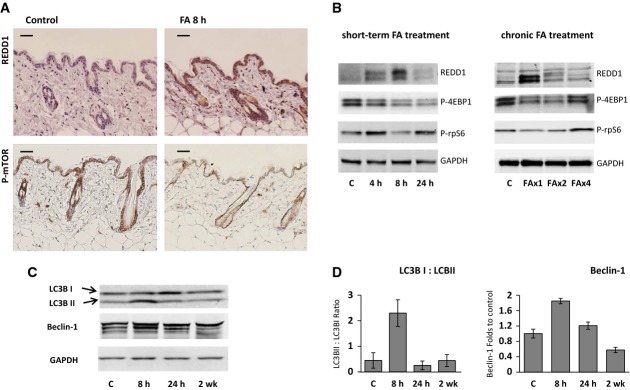
- A Immunohistochemical staining of mouse skin treated with acetone or FA for 8 h for REDD1 (upper panels) and phosphorylated mTOR-Ser2448 (lower panels). Scale bars are 20 μm.
- B Western blot analysis of REDD1 protein and phosphorylation of down-stream mTOR target proteins 4E-BP1 and rpS6 in murine epidermis. GAPDH is used as a normalization control.
- C, D Glucocorticoids induce autophagy in epidermis. Western blot analysis of Beclin-1 and conversion of light chain 3 (LC3) from LC3-I to LC3-II (C). Quantification of LC3-I to LC3-II conversion and Beclin-1 expression (D). The means ± SD were calculated using Western blots from two independent experiments (each lane is whole-cell protein from three pulled individual samples of epidermis).
