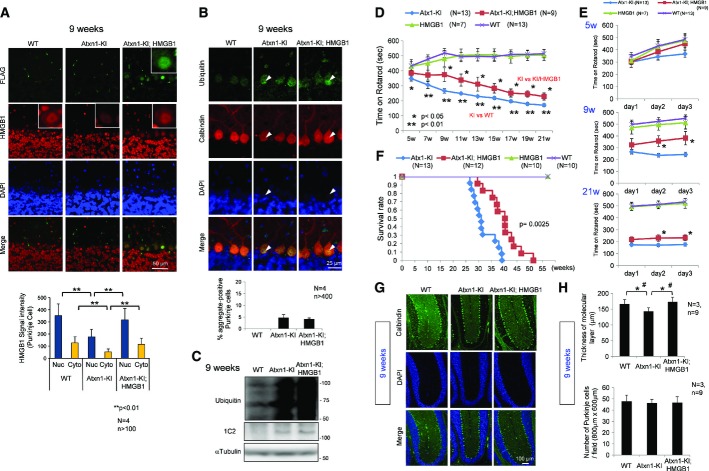
Figure 1. Symptomatic rescue of double-transgenic mice without decreased protein aggregation.
- The expression of exogenous HMGB1-FLAG (detected with an anti-FLAG antibody) and endogenous+exogenous HMGB1 (detected with an anti-HMGB1 antibody) was tested by immunohistochemical analysis. Nuclear and cytoplasmic signals were reduced in Atxn1-KI mice but restored in double-transgenic mice. The mean ± SD are shown in the lower graph.
- Aggregate formation was tested by immunohistochemical analysis of cerebellar tissues of background C57BL/6 mice, mutant Atxn1-KI mice and double-transgenic mice. Ubiquitin-positive aggregates were observed in mutant Atxn1-KI mice and double-transgenic mice (upper panels); the ratio of aggregate-positive Purkinje cells did not differ between the four mutant Atxn1-KI mice and the four double-transgenic mice (lower graph). The data are presented as mean ± SD.
- Western blot analysis with anti-ubiquitin antibody confirmed that aggregate formation was similar in mutant Atxn1-KI mice and double-transgenic mice.
- The rotarod performance test revealed improvement in the motor activity of double-transgenic mice over that of mutant Atxn1-KI mice. The time on rotarod was the mean value of the times from day 1 to day 3. The symptomatic onset in mutant Atxn1-KI mice was 7 weeks; improvement in double-transgenic mice lasted from 9 to 21 weeks. The data are presented as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed with the Bonferroni–Dunn test and Student's t-test.
- Details of the rotarod performance of the three genotypes of mice (WT, Atxn1-KI and double-transgenic) from day 1 to day 3 at 5, 9 and 21 weeks. The data are presented as mean ± SD.
- The survival rates of the four genotypes of mice. The mean and maximum lifespans of double-transgenic mice were nearly 30% longer than those of mutant Atxn1-KI mice. The 50% survival duration was extended from 217 days (Atxn1-KI) to 282 days (Atxn1-KI;HMGB1), and the maximum survival duration was extended from 274 days (Atxn1-KI) to 360 days (Atxn1-KI;HMGB1). The effect of HMGB1 on the lifespan was assessed by Kaplan–Meier analysis, and the end-point postponement was significant in the log-rank test (P = 0.0025).
- Histological evaluation of the double-transgenic mice.
- Quantitative analysis of histological parameters in the three groups of mice showed that reduction in the molecular layer thickness was reversed in double-transgenic mice (upper graph; Student's t-test, P < 0.05). The mean thickness was quantified in more than 10 visual fields per mouse, and the mean ± SD was calculated for nine mice in each group. The number of Purkinje cells, similarly calculated, was not changed in mutant Atxn1-KI mice or in double-transgenic mice (lower graph). The data are presented as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05 in Student's t-test, #P < 0.05 in one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey's HSD (honestly significant difference) test.
Source data are available online for this figure.