Figure 6.
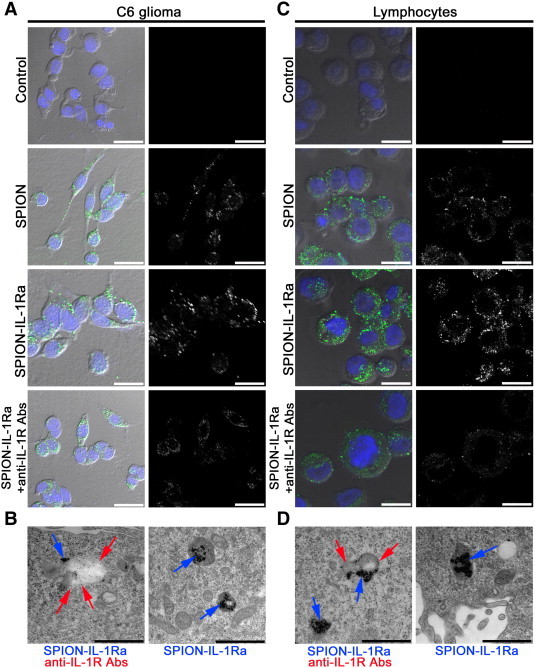
Interaction of the magnetic conjugates of IL-1Ra with C6 cells or lymphocytes. (A) Confocal microscopy images of the C6 cells following 24 hours of incubation with PBS, SPIONs (150 μg/ml), and SPION–IL-1Ra conjugates (150 μg/ml). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Magnetic nanoparticles were detected by reflecting laser scanning at 488 nm (green). Scale bar, 25 μm. For analysis of the receptor-mediated endocytosis, C6 cells were also incubated with anti–IL-1R monoclonal antibodies. (B) TEM of the C6 cell incubated for 24 hours with SPION–IL-1Ra conjugates. Electron dense nanoparticles were present in the cytoplasm of cells in the endosome-like structures (blue solid arrow). Receptors for IL-1 were detected with monoclonal anti–IL-1R antibodies (red solid arrow). Scale bar, 500 nm. (C) Confocal microscopy images of the rat lymphocytes following 24 hours of incubation with PBS, SPIONs (150 μg/ml), and SPION–IL-1Ra conjugates (150 μg/ml). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Magnetic nanoparticles are represented in the cytoplasm as green dots. Scale bar, 25 μm. For analysis of the receptor-mediated endocytosis, C6 cells were also incubated with anti–IL-1R monoclonal antibodies. (D) TEM of the lymphocyte incubated for 24 hours with SPION–IL-1Ra conjugates (blue arrows). Receptors for IL-1 were detected with monoclonal anti–IL-1R antibodies (red arrows). Scale bar, 500 nm.
