Figure 2.
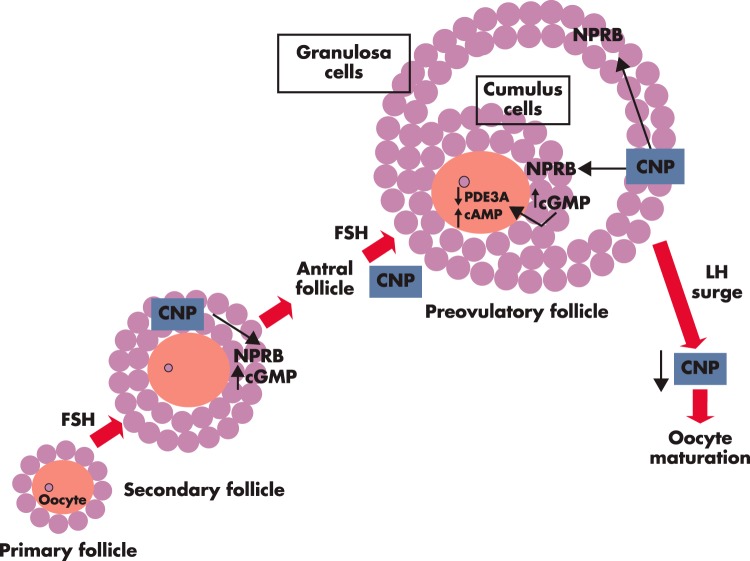
CNP is an intraovarian factor important for preantral and antral follicle growth as well as for oocyte maturation inhibition. Based on murine studies, CNP is secreted by granulosa cells of secondary and antral follicles in response to FSH stimulation. CNP acts through its receptor NPRB, expressed in granulosa cells of secondary follicles, to increase cGMP production and to stimulate follicle development (38). In addition, CNP acts through its receptor, expressed in cumulus cells of antral and preovulatory follicles, to increase cGMP production. Cumulus cell-produced cGMP, after transporting to oocytes through gap junctions, inhibits the activity of the phosphodiesterase 3A (PDE3A) enzyme, leading to increased intra-oocyte cAMP levels, thus suppressing oocyte maturation (30). The preovulatory LH surge decreases CNP levels in the preovulatory follicles and allows meiotic maturation of preovulatory oocytes (32).