Figure 3.
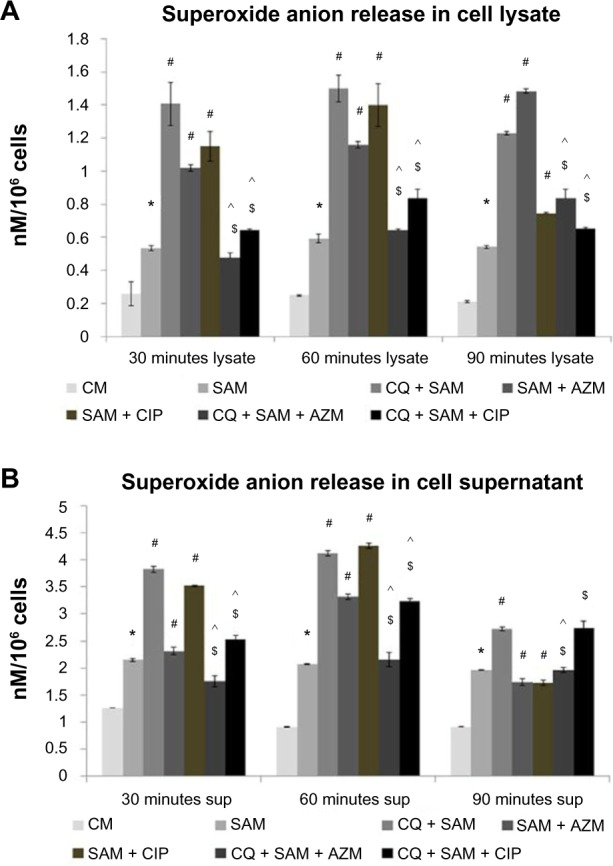
Effect of chloroquine (CQ) and antibiotic treatment on Staphylococcus aureus infection in the lysate and supernatant of murine peritoneal macrophages. The lysate (A) and supernatant (sup) (B) after time-dependent phagocytosis in the presence or absence of CQ or antibiotics were used to determine the release of superoxide anion.
Notes: Superoxide anion release is expressed in terms of nM/106 cells. Results are presented as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. *Significant difference with respect to CM; #significant difference with respect to SAM; ^significant difference with respect to CQ plus S. aureus-infected macrophages at the P<0.05 level of significance; $significant difference with respect to either ciprofloxacin (CIP) or azithromycin (AZM) plus S. aureus-infected macrophages.
Abbreviations: CM, control macrophages; CQ + SAM, chloroquine-pretreated plus S. aureus-infected macrophages; CQ + SAM + AZM, chloroquine-pretreated macrophages infected with S. aureus and then treated with azithromycin; CQ + SAM + CIP, chloroquine-pretreated macrophages infected with S. aureus and then treated with ciprofloxacin; SAM, S. aureus-infected macrophages; SAM + AZM, S. aureus-infected macrophages treated with azithromycin; SAM + CIP, S. aureus-infected macrophages treated with ciprofloxacin.
