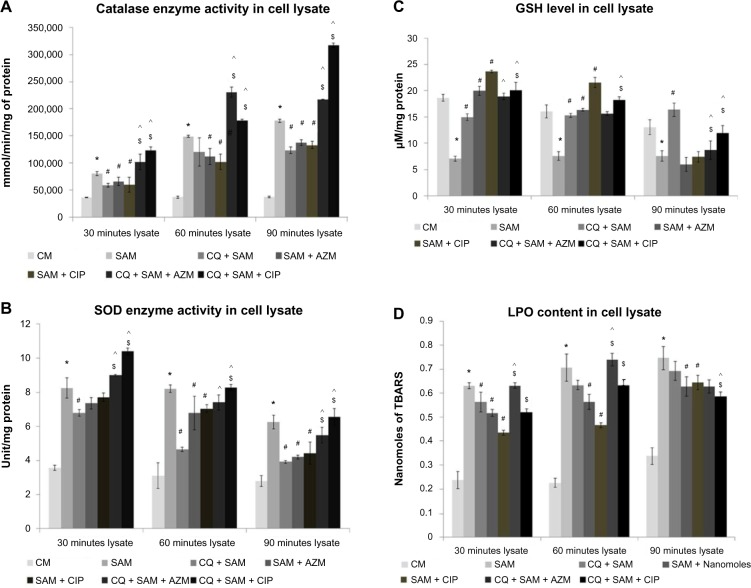
Figure 6.
Effect of chloroquine (CQ) and antibiotic treatment on Staphylococcus aureus infection-induced alteration in catalase, superoxide dismutase (SOD) enzyme activity, glutathione (GSH) level, and lipid peroxidation (LPO) content in the lysate in murine peritoneal macrophages. The cell-free lysate was recovered after time-dependent phagocytosis in the presence or absence of CQ or antibiotic treatment, as described in the “Methods and materials” section, and were used to determine the catalase (A), SOD enzyme activity (B), GSH level (C), and LPO content (D) in the lysate.
Notes: Catalase enzyme activity was measured in the presence of 15 μmoles of H2O2/ml of phosphate buffer and is expressed in terms of millimoles/minute mg protein (A); SOD activity is expressed in terms of SOD units/mg protein (B); GSH content is expressed in terms of μM/mg protein (C); and LPO content is expressed in terms of nmol of thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS) (D). Results are shown as mean ± standard deviation of three independent experiments. *significant difference with respect to CM; #significant difference with respect to SAM; ^significant difference with respect to CQ plus S. aureus-infected macrophages at the P<0.05 level of significance; $significant difference with respect to either ciprofloxacin (CIP) or azithromycin (AZM) plus S. aureus-infected macrophages.
Abbreviations: CM, control macrophages; CQ + SAM, chloroquine-pretreated plus S. aureus-infected macrophages; CQ + SAM + AZM, chloroquine-pretreated macrophages infected with S. aureus and then treated with azithromycin; CQ + SAM + CIP, chloroquine-pretreated macrophages infected with S. aureus and then treated with ciprofloxacin; SAM, S. aureus-infected macrophages; SAM + AZM, S. aureus-infected macrophages treated with azithromycin; SAM + CIP, S. aureus-infected macrophages treated with ciprofloxacin.