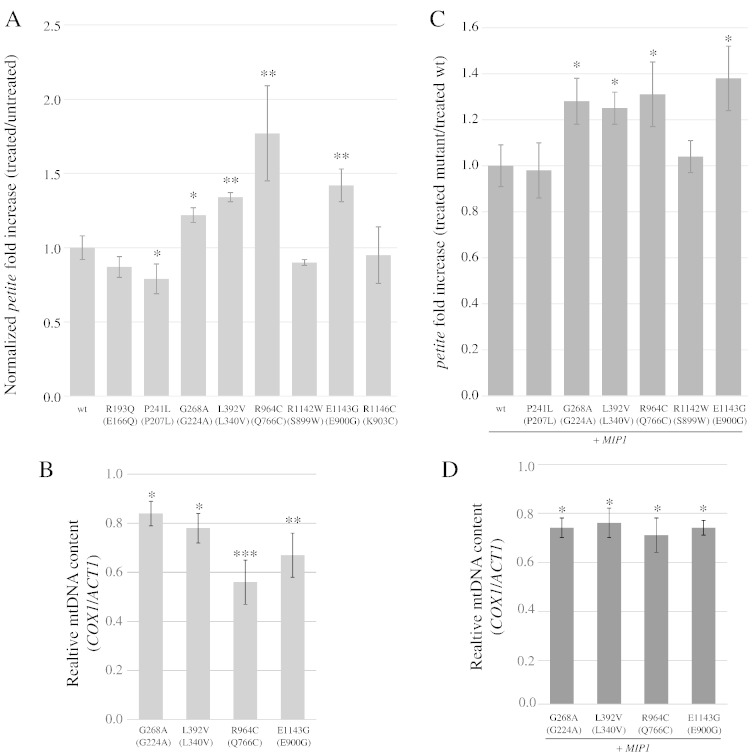
Fig. 4.
(A) Normalized petite fold increase of strains treated with 1 mM d4T relative to untreated strains. For each mutant, the normalized petite fold increase is the mean of the ratios [(petite frequency of treated mutant strain)/(petite frequency of untreated mutant strain)]/[(petite frequency of treated wt strain)/(petite frequency of untreated wt strain)] (see also Supplementary Table 6). For mutant strains harboring human substitutions P193Q, R964C, R1142W and R1146C, the frequencies were compared to strains harboring the corresponding mip1 humanized allele. (B) mtDNA levels in strains with a higher normalized petite fold increase after treatment with 1 mM d4T. The ratio COX1/ACT1 was normalized to 1 for wild type strain. (C) Normalized petite fold increase of heteroallelic strains treated with 2 mM d4T compared to homoallelic strain treated with 2 mM d4T. For each mutant, the normalized petite fold increase is the ratio (petite frequency of treated mutant strain/petite frequency of treated wt strain) (See also Supplementary Table 7). For mutant MIP1/mip1 strains harboring human substitutions R964C, R1142W and R1146C, the frequencies were compared to strains harboring the corresponding MIP1/mip1 humanized allele. Statistical significance is as in Fig. 1. (D) mtDNA levels in heteroallelic strains with a higher petite fold increase after treatment with 2 mM d4T. The ratio COX1/ACT1 was normalized to 1 for homoallelic wild type strain.