Fig. 1.
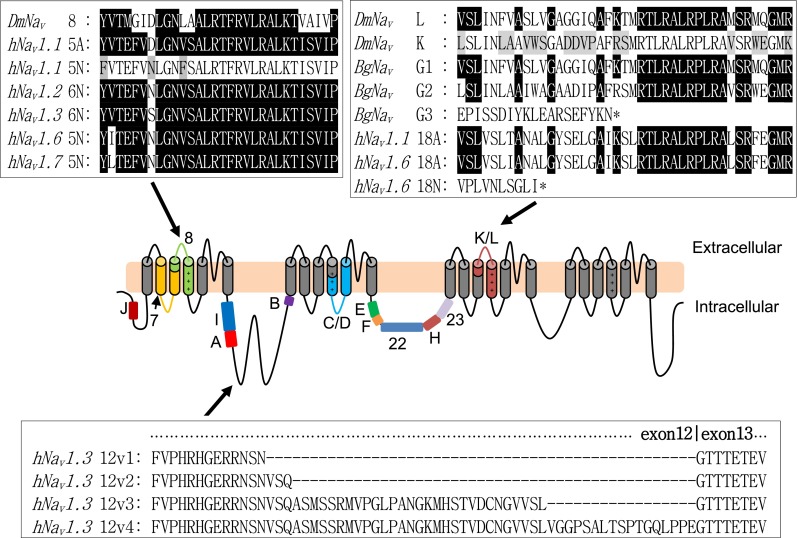
Schematic of the predicted topology of the voltage-gated sodium channel showing approximate locations of Drosophila spliced exons. Cytoplasmic DmNa v exons J, 7, 8, I, A, B, E, F, 22, H, 23 are optional, while exons C/D and K/L are mutually exclusive. DmNa v exon 8 is conserved in human Navs as mutually exclusive spliced exons 5A and 5N (6A and 6N in hNa v 1.2 and hNa v 1.3 due to different exon numbering in the consensus gene sequence), and identical residues are shown in black boxes. Exon 5A and 5N of hNa v 1.1 differ by 3 amino acids, shown in grey boxes in the 5N sequence. Mutually exclusive DmNa v spliced exon L and cockroach BgNa v exon G1 are identical and are conserved in human: exon 18A of hNa v 1.1 and hNa v 1.6. DmNa v exons K and L differ by 16/41 residues (shown in grey boxes in the exon K sequence). Inclusion of BgNa v exon G3 and hNa v 1.6 exon 18N generated a truncated channel. Exon 12 of hNa v 1.3 is located in the intracellular loop between domains I and II. By using different splice donor sites in exon 12, four spliced variants, 12v1, 12v2, 12v3, and 12v4 can be generated. The amino acid sequences are obtained as follows: DmNa v 8, K, and L [15]; hNa v 5A and 5N [61]; hNa v 1.6 18A and 18N [23]; BgNa v G1, G2, and G3 [20]; hNa v 1.3 12v1, 12v2, 12v3, and 12v4 [30]
