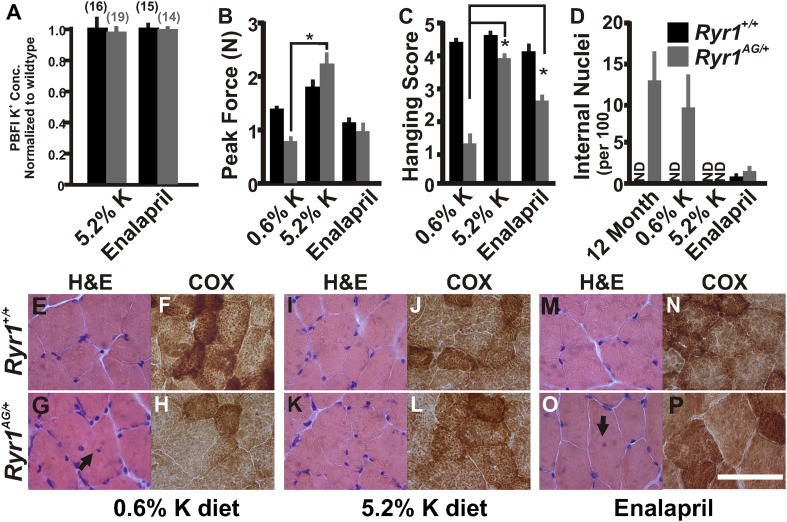
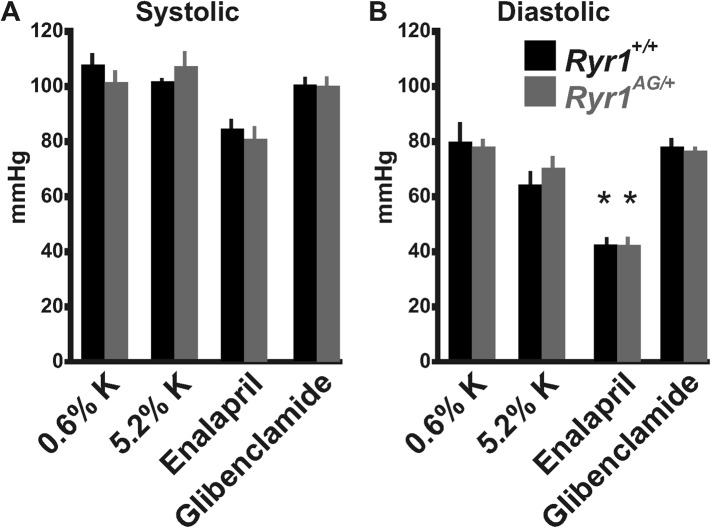
Figure 6. Increased potassium diet can rescue muscle strength and reverse the CCD histology and myopathy.
(A) Normalized internal potassium concentrations of soleus muscle from 2-month old Ryr1+/+ and Ryr1AG/+ mice fed 0.6% K+ diet for 4 weeks, then placed on 5.2% K+ diet or 0.6% diet + enalapril for 4 weeks, and then bath exposed to different extracellular potassium concentrations. (B, C) Average grip strength (B, five trials/mouse and 5 mice/set; p values <0.001) and in vivo hanging task (C, 10 trials/mouse, n = 5 per set; p values <0.001) assayed from 2-month old Ryr1+/+ (black bar) and Ryr1AG/+ (grey bar) mice maintained for 4 weeks on control 0.6% K+ diet, 5.2% K+ diet, or 0.6% K+ diet supplemented with enalapril. (D) Quantification of number of internalized nuclei per 100 myofibers in 12-month old mice or in 2-month old mice maintained for 4 weeks on control 0.6% K+ diet, 5.2% K+ diet, or 0.6% K+ diet supplemented with enalapril (n = 10 per muscle, n = 3 per set of muscles for total of n = 30; p values <0.001). (E–P) Vastus lateralis myofibers from 2-month old Ryr1+/+ and Ryr1AG/+ mice maintained for 4 weeks on control 0.6% K+ diet, 5.2% K+ diet, or 0.6% K+ diet supplemented with enalapril. Cross-sections stained with H&E (left panels) and COX (right panels). Ryr1AG/+ mice on 5.2% K diet show increased COX staining and no internalized nuclei, similar to Ryr1+/+. These pathological features are still observed in Ryr1AG/+ mice on 0.6% K+ diets. Enalapril increases COX staining but some internalized nuclei are observed, even in Ryr1+/+. Scale bar = 50 μm; error bars as standard error of the mean (SEM).