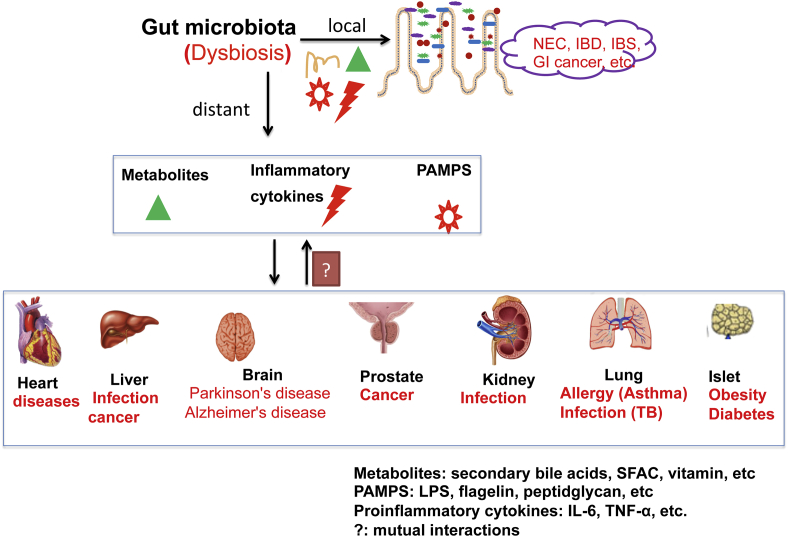
Figure 1.
Host-bacterial interactions that could potentially mediate the gut microbiota human diseases in local intestine and distant organs. Gut microbiota influences amino acid bioavailability, is a source of metabolites (SBA, SCFA, PAMPs). Dysbiosis is associated with dysfunction of intestinal barriers and enhances proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-1β, and IL-8). All these factors could potentially influence pathogenesis and progression of human diseases.