Figure 1.
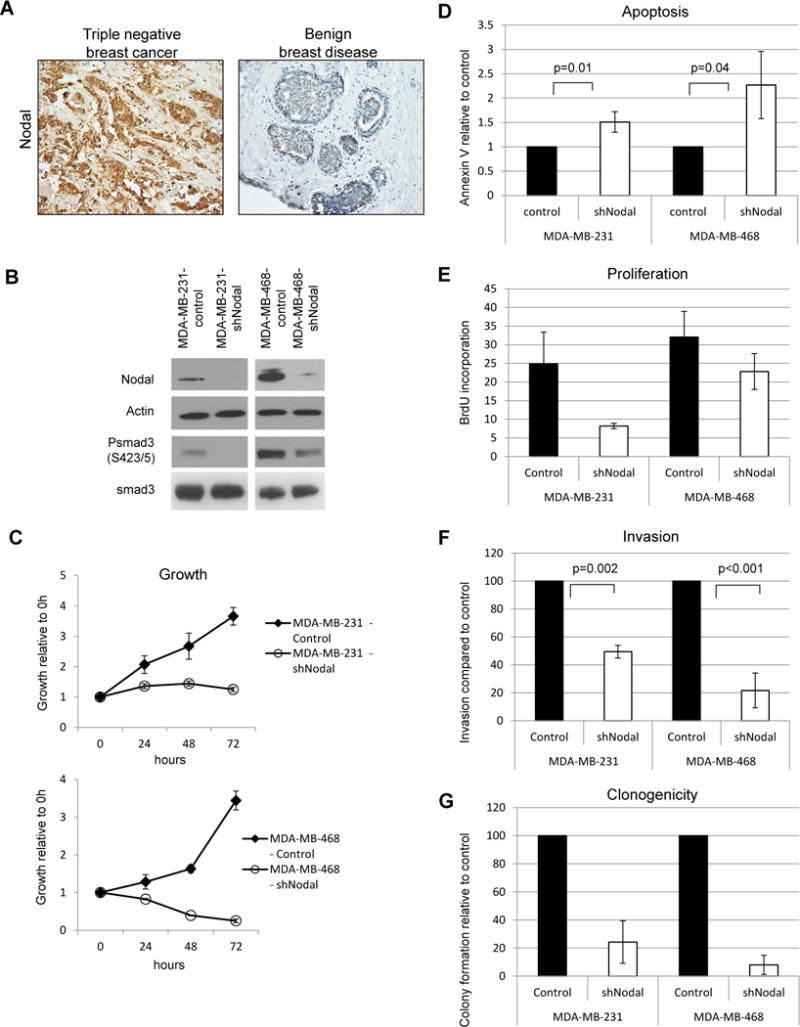
Nodal knockdown impairs growth and aggressive behavior in human breast cancer cell lines. A) Representative immunohistochemistry results show increased expression (brown staining) of Nodal in a triple negative breast cancer biopsy section compared to a biopsy section of benign breast disease (200X original magnification). A) Western blot demonstrating Nodal knockdown and smad 3 phosphorylation status in human breast cancer cell lines. Data are representative of 3 experiments. B) Cell growth curves for knockdown and control cell lines. Error bars represent standard deviation. C) Apoptosis in Nodal knockdown and control cells was measured by Annexin V staining and flow cytometry. Error bars represent standard deviation. D) Proliferation in Nodal knockdown and control cells. Cells were cultured in the presence of BrdU for 30 minutes prior to fixation and analyzed by flow cytometry. N=3 for each cell type; error bars represent standard deviation. E) Invasive potential of Nodal knockdown and control cells. Percent invasion was calculated based on the number of cells seeded and normalized to controls. F) Colony formation in soft agar after 3 weeks. Colonies were counted and normalized to controls.
