Figure 3.
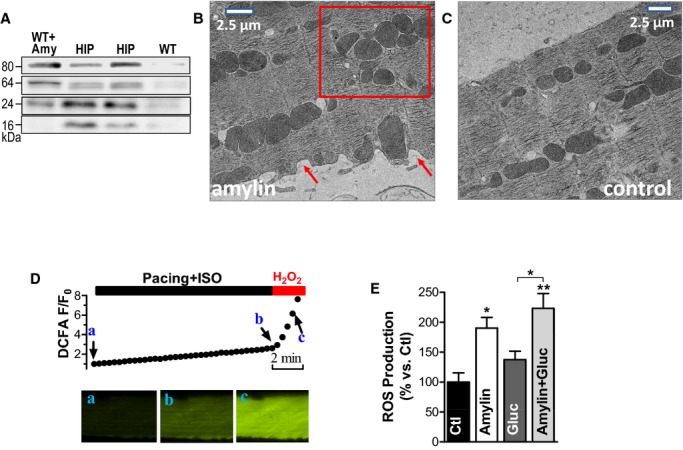
The interaction of oligomeric amylin with sarcolemma causes oxidative stress in cardiac myocytes. A, Western blot with an antiamylin antibody on lysates from control myocytes incubated with preformed amylin aggregates (WT+Amy), HIP rats myocytes (HIP), and control WT cells (WT). Oligomers were preformed by incubating 50 μmol/L exogenous human amylin for 2 hours at room temperature. B and C, Representative transmission EM images of WT rat cardiac myocytes incubated with 50 μmol/L oligomerized human amylin for 2 hours (B) and control myocytes (C). Arrows point to alterations in sarcolemmal structure. The square guides the eye to the mitochondrial disarrangement. D, Representative example of ROS production measurement with the fluorescent indicator CM‐H2DCFA. Myocytes loaded with CM‐H2DCFA were electrically stimulated at 1 Hz in the presence of isoproterenol (ISO, 1 μmol/L), which increased CM‐H2DCFA fluorescence (from point a to point b), indicating ROS (H2O2) production. At the end, pacing was stopped and H2O2 (1 mmol/L) was washed in to verify the specificity of the signal (increased fluorescence from b to c). ROS production was measured as the slope of fluorescence increase between the points a and b. E, ROS production was compared in control myocytes (Ctl; 11 myocytes from 3 rats) and myocytes incubated with preformed amylin oligomers (amylin; 8 myocytes, 3 rats), 400 mg/dL glucose (gluc; 7 myocytes, 3 rats), and a combination of glucose (400 mg/dL) and preformed amylin oligomers (amylin+gluc; 7 myocytes, 3 rats). *P<0.05, **P<0.01. CM‐H2DCFA indicates 5‐(and‐6)‐chloromethyl‐20,70‐dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate acetyl ester; EM, electron microscopy; HIP, human amylin in the pancreas; ROS, reactive oxygen species; WT, wild‐type.
