Figure 6.
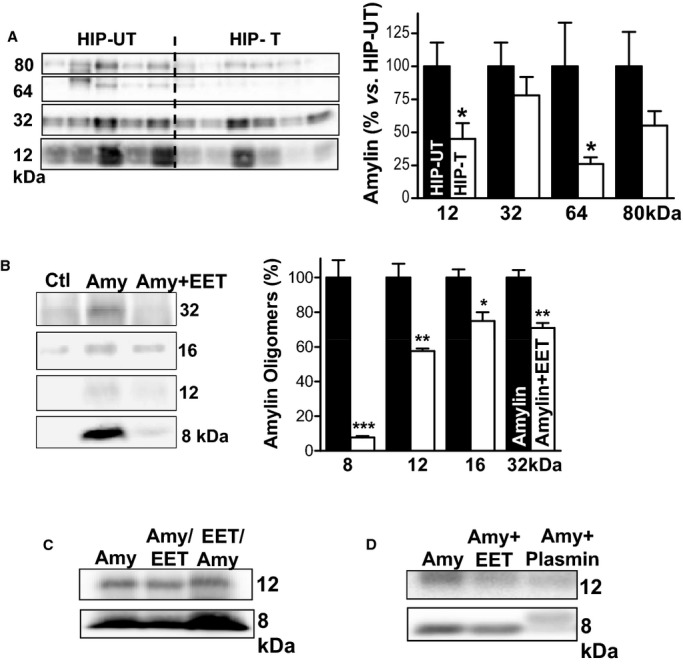
EETs reduce the level of amylin oligomers circulating in the blood. A, Representative (of 4 experiments) Western blot with an antiamylin antibody on whole blood cell lysates from HIP rats in the treated (T) and untreated (UT) groups. Bottom panel shows the band intensity analysis for these experiments. B, Representative (of 3 experiments) Western blot with an antiamylin antibody on ventricular myocyte lysates from control rats. Before lysis, myocytes were incubated for 2 hours in the absence (Ctl) or in the presence of 50 μmol/L recombinant human amylin (Amy). Myocytes in the Amy+EET column were incubated with 50 μmol/L human amylin and 5 μmol/L 14,15‐EET. Co‐incubation with EETs reduced the attachment of amylin oligomers to cardiac myocytes. Bottom panel shows the band intensity analysis. C, The effect of 5 μmol/L 14,15‐EET on amylin attachment to the sarcolemma when added before (EET/Amy) or after (Amy/EET) incubation of myocytes with oligomerized amylin. D, Representative Western blot showing that 14,15‐EETs and plasmin (both 5 μmol/L) limit oligomerization of recombinant human amylin in saline solution (50 μmol/L amylin; 2 to 3 hours incubation time). *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. EETs indicates epoxyeicosatrienoic acids; HIP, human amylin in the pancreas.
