Figure 6. Germ-free T5KO mice are highly susceptibility to early AIEC LF82 infection.
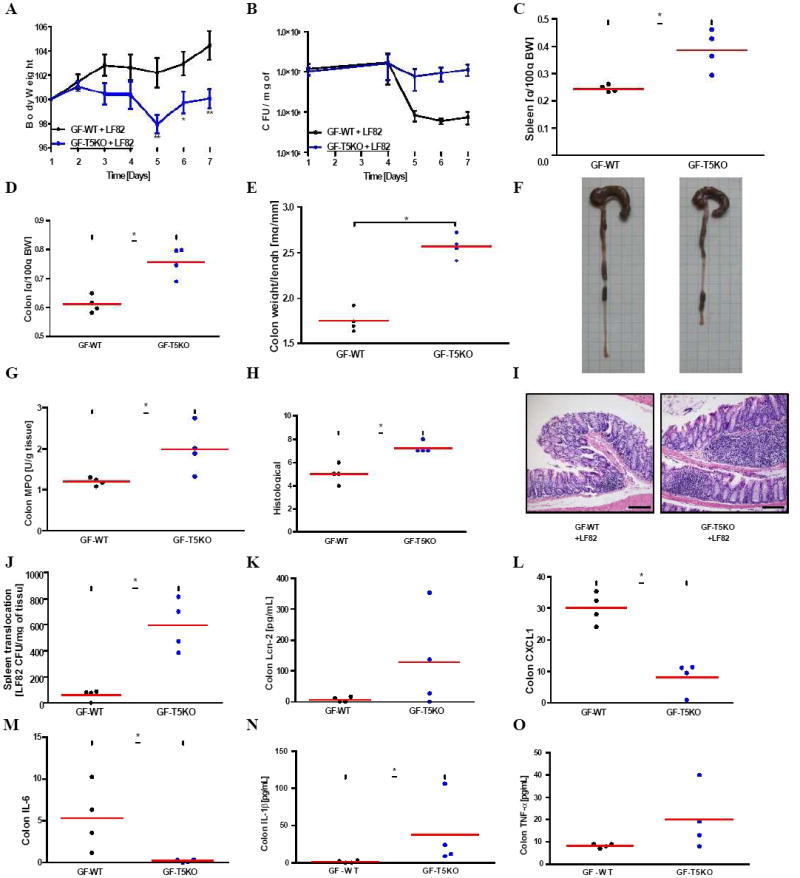
Germ-free wild-type and T5KO mice (n=4 mice per group) were orally infected with 107 flagellate AIEC LF82 bacteria. (A) Body mass was monitored daily during the treatment. (B) Numeration of AIEC LF82 present in the WT or T5KO mouse stool from day 1 to day 7 post infection. (C) Following euthanasia, spleen was isolated and mass measured. (D) Colon mass. (E) Ratio between colon weight and colon length. (F) Gross picture of colon. (G) Colon MPO activity. (H-I) Histological score and representative H&E stained colon (magnification, 100×). (J) Bacterial translocation by numbering AIEC LF82 CFU present in the spleen at day 7 post infection. (K-O) Colon was cultured for 24h, at which time supernatant was assayed for Lcn-2 (K) and several pro-inflammatory cytokines, namely CXCL1 (L), IL-6 (M), IL-1β (N) and TNF-α (O), by ELISA. * p<0.05. Related materials can be found in supplementary figure 4.
