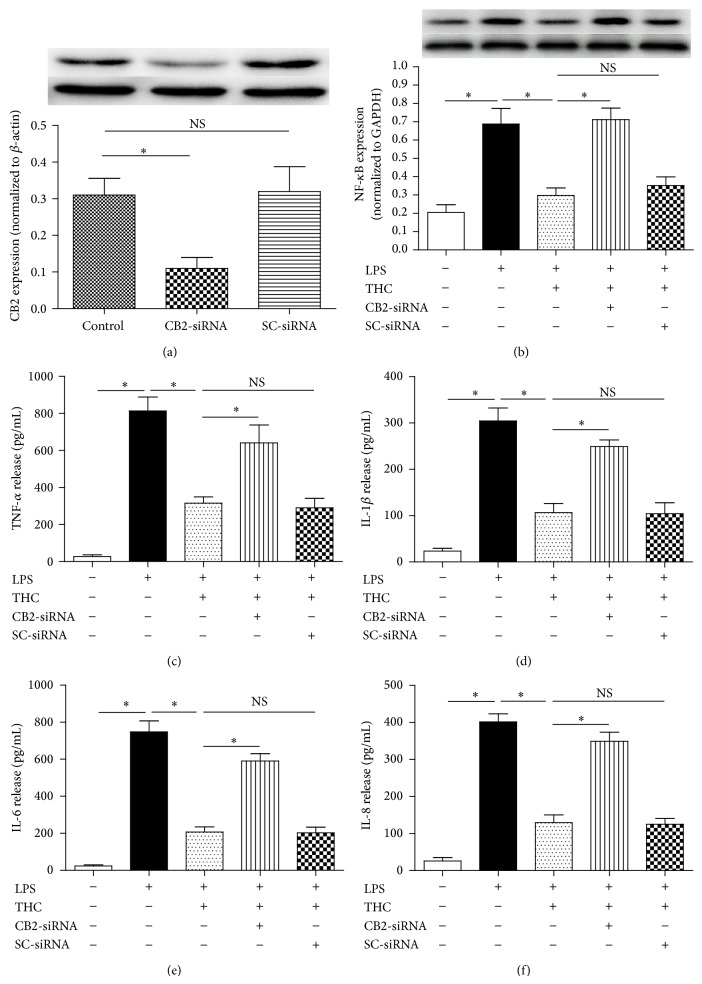
Figure 6.
CB2-siRNA reversed THC-induced decrease of inflammatory factors release. MG-63 cells were assigned into five groups, control (no LPS, THC, or siRNA): cultured in drug-free medium; LPS: cells exposed to 10 ng/mL LPS for 24 h; THC + LPS: cells exposed to 5 μM THC plus 10 ng/mL LPS for 24 h; CB2-siRNA + THC + LPS: cells incubated with CB2-siRNA for 24 h and then exposed to 5 μM THC plus 10 ng/mL LPS for 24 h; scrambled siRNA (SC-siRNA) + THC + LPS: cells incubated with SC-siRNA for 24 h and then exposed to 5 μM THC plus 10 ng/mL LPS for 24 h. (a) CB2-siRNA significantly downregulated the expression of CB2 receptor, assessed by western blot (n = 3). (b) CB2-siRNA significantly reversed THC-induced effect on NF-κB expression (n = 6). (c)–(f) CB2-siRNA significantly reversed THC-induced effects on the release of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 (n = 6). Results are means ± SD. *: P < 0.05; NS: no significance.