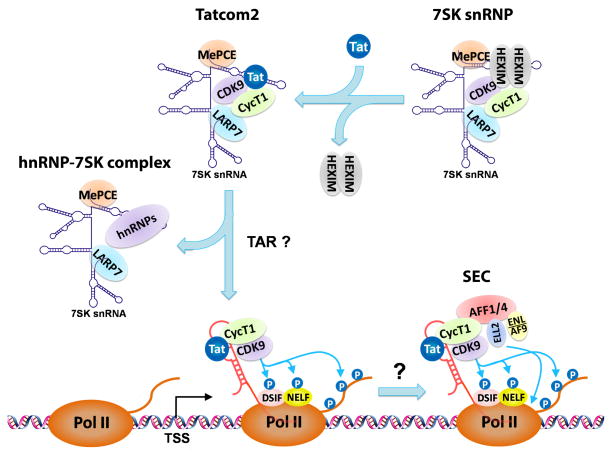
Fig. 3. Tat induces transfer of P-TEFb from 7SK snRNP via possibly Tatcom2 to SEC, where P-TEFb cooperates with ELL2 to synergistically activate HIV LTR transcription.
Tat is known to target the 7SK snRNP to capture P-TEFb and release HEXIM1. The Tatcom2 complex, whose composition is similar to that of 7SK snRNP except for the substitution of HEXIM1 with Tat, could be a reaction intermediate before the emergence of HIV TAR RNA. Once TAR is produced, P-TEFb and Tat are transferred onto the TAR structure, and through a still unknown mechanism, nucleate the formation of the multi-subunit SEC complex. Besides P-TEFb, which phosphorylates the Pol II CTD and negative elongation factors NELF and DSIF to antagonize their inhibitory effects, SEC also contains another well-characterized elongation stimulatory factor ELL2, which directly enhances the catalytic activity of Pol II. By acting on the same Pol II enzyme, P-TEFb and ELL2 synergistically activate HIV transcription.